Fig. 3.
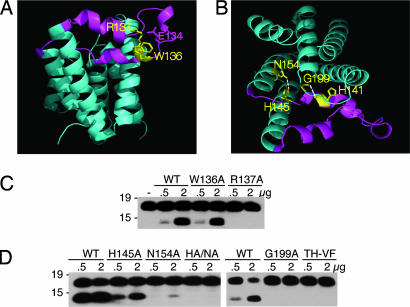
Disrupting L1 loop:core interactions reduces protease activity. (A) Side view of GlpG (2NRF) with the L1 loop highlighted in magenta and the conserved WR motif within the L1 loop shown in yellow. R137 makes a series of hydrogen bonds to upper regions of the loop and to E134. (B) Top view of GlpG (2NRF) with the L1 loop:core hydrogen bonds between N154 of transmembrane domain 2 and H145 of the L1 loop, and the backbone of H141 of the loop and G199 above helix 4. (C) Mutagenesis of W136 had a mild effect on protease activity of GlpG, whereas changing R137 to alanine abolished protease activity. Western blot analysis of C100Spitz-Flag cleavage is shown. (D) The effect of disrupting L1 loop:core contacts by mutagenesis of H145 and N154 individually to alanine, or their double mutant (HA/NA), as well as G199 to alanine and H141 to phenylalanine with the neighboring T140 to valine (TH-VF), tested for proteolytic activity.