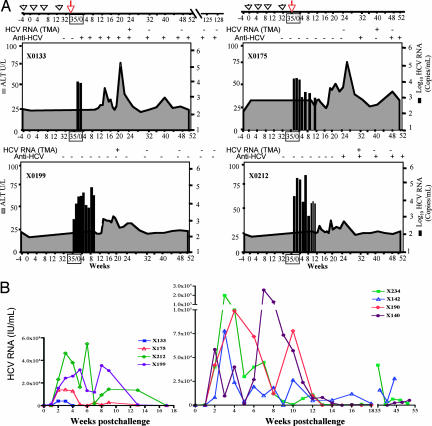
Fig. 3.
The time course of HCV infection in HCV-LP-immunized chimpanzees. (A) Four chimpanzees were immunized four times over 32 weeks with HCV-LPs. Three weeks after the fourth dose (35/0), the chimpanzees were challenged with homologous HCV-CG1b strain. Arrowheads indicate immunization times and the arrow indicates the time of the HCV-CG1b challenge. HCV RNA titers and alanine transaminase (ALT) levels are shown. Black bars represent HCV RNA in log10(copies per milliliter) (right ordinates) and the lined gray zone represents ALT levels in units/ml (left ordinates). Anti-HCV seroconversion is indicated as − or + at the top of each graph. Some of the samples (negative by PCR) were tested for HCV RNA by transcription-mediated amplification (TMA) and the results are shown. Follow-up samples beyond 1 year after the challenge were available for TMA testing in chimpanzees X0133 and X0199. (B) Comparison of HCV viremia between naïve and HCV-LP-immunized chimpanzees after the challenge. Previously, four control chimpanzees were infected with HCV-CG1b strain at a dose of 3–10 CID50 (15, 32); the courses of HCV viremia are shown (Right). The viral titers were all converted to units per milliliter for ease of comparison because HCV quantification was done with different assays. For comparison, the viremia courses of the four HCV-LP-immunized chimpanzees are shown together (Left).