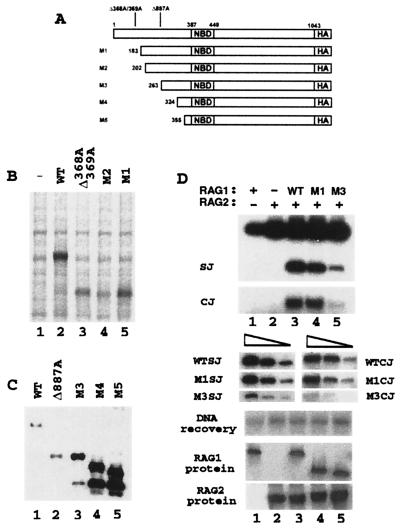
Figure 4.
RAG1 Δ368A/369A is initiated from methionine 183, and Rag1 Δ887A is initiated from methionine 263. (A) Diagram of 3′ HA-tagged RAG1 constructs. (B) HA-tagged forms of wild-type (WT) RAG1 (lane 2), Δ368A/369A RAG1 (lane 3), methionine 202 RAG1 (M2; lane 4), and methionine 183 RAG1 (M1; lane 5) were isolated from 293T cells transiently transfected with equal amounts of plasmid and metabolically labeled with [35S]methionine and cysteine. (C) Western blot analysis using anti-HA antibody 12CA5 to detect 3′ HA-tagged RAG1 isoforms coprecipitated with gstRAG (amino acids 1–383) after cotransfection in 293T cells. Lanes: 1, wild-type RAG1; 2, Δ887A RAG1; 3, methionine 263 RAG1 (M3); 4, methionine 324 RAG1 (M4); and 5, methionine 355 RAG1 (M5). (D) Recombination assays for full-length RAG1 and the M1 and M3 truncated proteins (the recovered plasmid was used at a 1:50 dilution). Ten micrograms of full-length plasmid was transfected into cells, and 4 μg of M1- and M3-expressing pEBB plasmid was used to attain comparable levels of protein expression. Serial dilutions (1:10, 1:40, 1:100) are shown, as well as Western blots demonstrating RAG1 protein expression (detected with RAG1 antibody R1P7, a kind gift from the Schatz lab) and gstRAG2 (amino acids 1–383) protein levels (detected by using an anti-gst antibody).