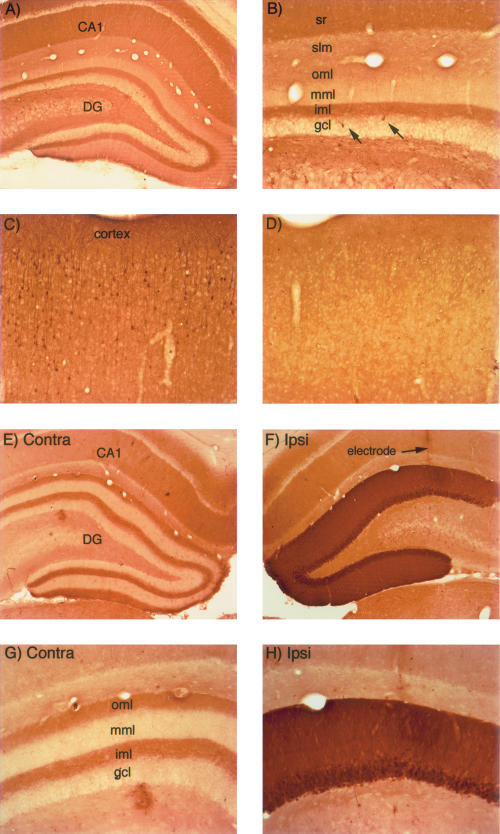
Figure 1.
Activity-dependent regulation of ERK1/2 phosphorylation in rats. (A,B) pattern of immunostaining for p-ERK in the hippocampus in a rat that was perfused immediately after receiving a fatal anesthetic dose (that is, the rat was awake until ∼ 3 min before perfusion). (C) Pattern of immunostaining for p-ERK in the cerebral cortex of the rat illustrated in A and B. Note heavily stained individual neurons. (D) Pattern of immunostaining for p-ERK in the cerebral cortex of a rat that had been anesthetized for ∼ 2.5 h during a neurophysiological experiment. (E) Pattern of immunostaining on the control (nonstimulated) side of the hippocampus of a rat that had been anesthetized for ∼ 2.5 h during a neurophysiological experiment. (F) Induction of ERK1/2 phosphorylation following induction of LTP using 400 Hz stimulation. The track of the micropipette recording electrode is indicated. (G,H) Higher magnification views of the dorsal blade of the dentate gyrus from the sections illustrated in E and F. Note the laminar pattern of staining for p-ERK in the molecular layer of the control dentate gyrus and the dramatic increase in immunostaining on the stimulated side. CA1 = CA1 region of the hippocampus; (DG) dentate gyrus; (sr) stratum radiatum; (iml) inner molecular; (mml) middle molecular layer; (oml) outer molecular layer; and (slm) stratum lacunosum-moleculare.