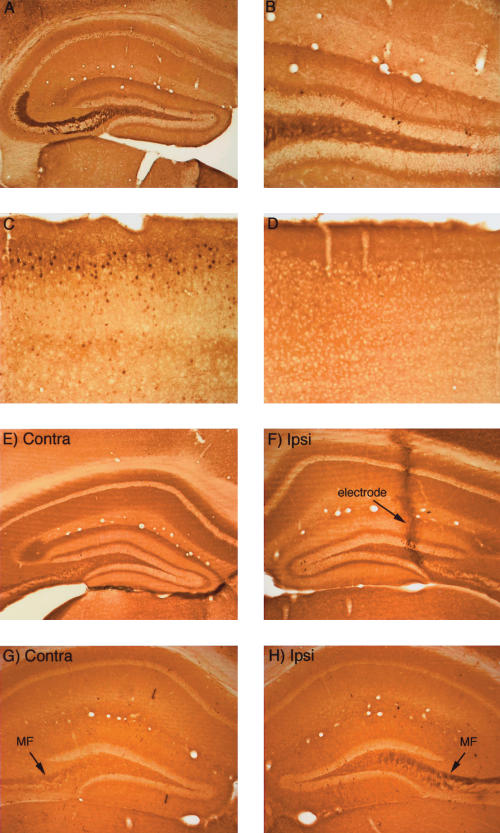
Figure 4.
Activity-dependent regulation of ERK1/2 phosphorylation in mice. (A,B) Pattern of immunostaining for p-ERK in the hippocampus in a mouse that was perfused immediately after receiving a fatal anesthetic dose (that is, the mouse was awake until ∼ 3 min before perfusion). (C) Pattern of immunostaining for p-ERK in the cerebral cortex of the mouse illustrated in A and B. Note heavily stained individual neurons. (D) Pattern of immunostaining for p-ERK in the cerebral cortex of a mouse that had been anesthetized for ∼ 2.5 h during a neurophysiological experiment. (E) Pattern of immunostaining on the control (nonstimulated) side of the hippocampus of a mouse that had been anesthetized for ∼ 2.5 h during a neurophysiological experiment. (F) Pattern of immunostaining following induction of LTP using 400-hz stimulation. Note the lack of an increase in immunostaining for p-ERK. The track of the micropipette recording electrode is indicated. (G) Pattern of immunostaining for p-ERK on the control (nonstimulated) side of the hippocampus of a mouse that had been anesthetized for ∼ 2.5 h during a neurophysiological experiment. (H) Lack of induction of ERK1/2 phosphorylation following delivery of 400 Hz stimulation for 2 h. Note, however, that immunostaining in the mossy fiber (MF) layer is higher on the stimulated side.