Figure 6.
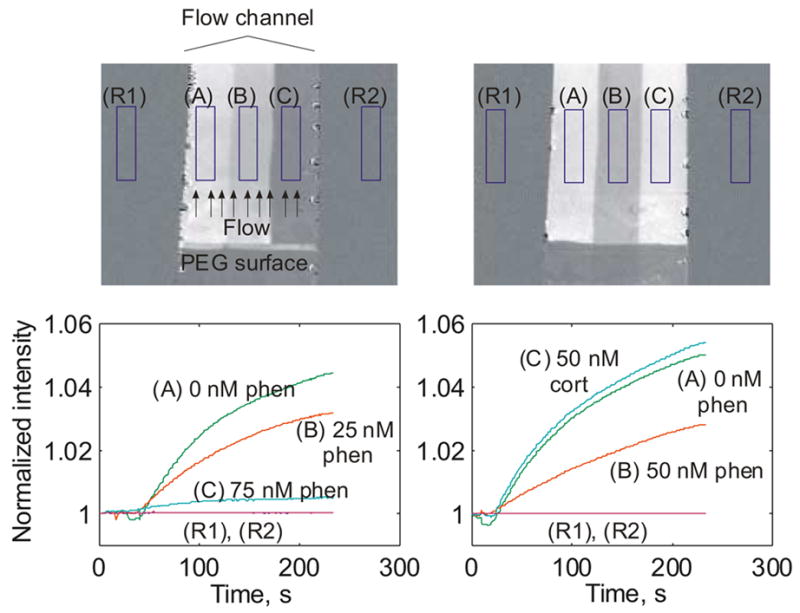
Imaging assays for phenytoin. Gold surfaces were coated with a nonfouling layer (dark region on bottom) and BSA-phenytoin. Three fluid streams containing different concentrations of phenytoin mixed with 100 nM phenytoin antibody were flowed across the surface simultaneously. Sample streams remain distinct due to laminar flow. Over the ~250 second course of the experiment, the brightness of each region increases proportional to the amount of free antibody binding to the surface, and is expected to decrease with increasing analyte concentration. Experiments confirm this, with 0 nM phenytoin producing the highest binding rate, with 25 nM, 50 nM, and 75 nM phenytoin producing monotonically decreasing rates of binding. In the rightmost plot, specificity of response was tested by assaying a 50 nM cortisol solution. Binding similar to that for 0 nM phenytoin was observed, confirming specificity of the phenytoin antibody.
