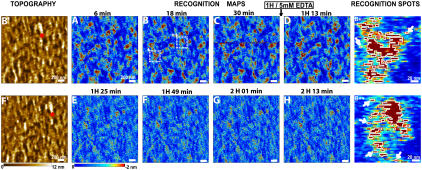
FIGURE 2.
Recognition images of a MyEnd cell surface obtained with VE-cadherin-Fc-functionalized tip. (A–C) During 1 h of scanning recognition maps of VE-cadherin domains remain unchanged. Then, 5 mM EDTA was very slowly (∼50 μl/min) injected in the fluid cell while scanning the sample. The first scan (D) did not reveal immediate changes in the recognition map. The recognition clusters disappeared as the active VE-cadherin-Fc cis-dimers on the AFM tip dissociated in inactive monomers, thereby abolishing specific VE-cadherin trans-interaction (E–H). Note that in Ca2+-rich conditions the previously blocked tip regains its functionality. (B′,F′) Topography images simultaneously recorded with B and F, respectively. After blocking experiments, topography (F′) remains unchanged—indicating that blocking does not affect membrane topography (compare B′ and F′). Red stars in B′ and F′ indicate the AFM scanner lateral drift of ∼5 nm/min. (B+, B++) Examples of recognition spots magnified from B (areas + and ++, respectively). Recognition areas are depicted by threshold analysis (threshold = −1.7 nm) and bordered by white lines. Single VE-cadherin cis-dimers can be clearly detected (arrows).