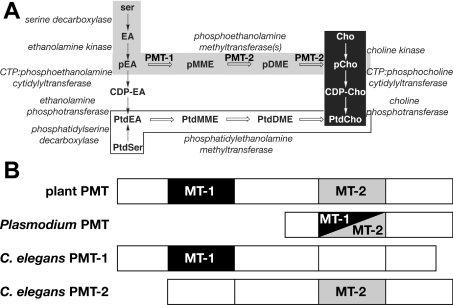
Figure 1. Overview of phosphatidylcholine biosynthesis.
(A) Phosphatidylcholine biosynthesis in different organisms. The de novo choline or Kennedy pathway (white on black), the Bremer–Greenberg pathway (black on white) and the phosphobase methylation pathway (black on grey) are shown. Metabolite names consist of a prefix (p, phospho; CDP-, cytidine 5′-diphosphate; or Ptd, phosphatidyl) and a core name (EA, ethanolamine; MME, monomethylethanolamine; DME, dimethylethanolamine; Cho, choline). (B) Overview of the domain organization and reactions catalysed by the PEAMT from plants, P. falciparum and C. elegans. Methyltransferase domains are indicated by shaded boxes. Methylation of phosphoethanolamine to P-MME is catalysed by the first methyltransferase domain (MT-1) and the next two methylation reactions that convert P-MME into phosphocholine are catalysed by the second methyltransferase domain (MT-2). The Plasmodium PEAMT uses a single domain (black/grey) to perform all three methylation reactions.