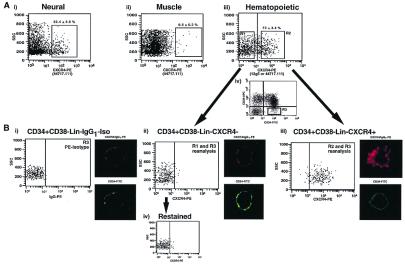
Figure 1.
Isolation of CXCR4+ and CXCR4− subfractions within primitive human hematopoietic populations. (A) A representative FACS analysis of human neuronal (i), muscle (ii), and CB cells (Lin−) (iii), stained with either 12 g5 or 44717.111 anti-human CXCR4 antibodies conjugated to PE. The percentage of CXCR4+ cells detected is given above each positive gate as the mean ± SEM of four (neural), two (muscle), and six (hematopoietic) different samples. CB Lin− cells stained with mouse IgG1 served as isotype to establish sorting gates for the purification of CXCR4− and CXCR4+ hematopoietic subpopulations indicated as R1 and R2, respectively (iii). Subpopulations of CD34+ CD38−Lin− cells were isolated by using the R3 sorting gate (iv). (B) CD34+ CD38−Lin− cells stained with IgG1-PE were analyzed by FACS and confocal to serve as a control (i). Fluorescence of control (i) was compared with purified CD34+ CD38−Lin−CXCR4− (R1 and R3) and CD34+ CD38−Lin−CXCR4+ (R2 and R3) cells, a measure of sort purity (ii and iii). Selected CXCR4− cells were restained for CXCR4 by using 12 g5 or 44717.111 and reanalyzed to verify the absence of any CXCR4+ cells (iv). For confocal microscopy, primitive CD34+ CD38−Lin− cells stained with isotype control, CD34+ CD38−Lin−CXCR4−, and CD34+ CD38−Lin−CXCR4+ cells were isolated by FACS and visualized with a Zeiss LSM-410 confocal microscope at random z-planes. Representative photographs depicting the PE and FITC fluorescence from CD34+ CD38−Lin− isotype control (i), CD34+ CD38−Lin−CXCR4− (ii), and CD34+ CD38−Lin−CXCR4+ (iii) cells are presented along side each corresponding population reanalyzed by FACS (n = 4).