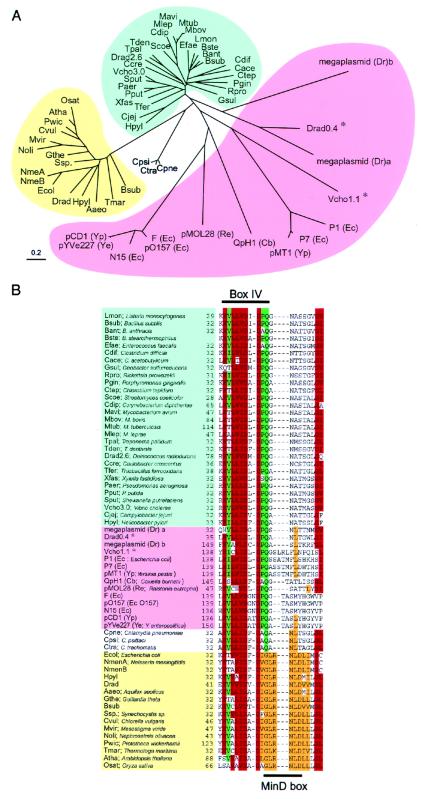
Figure 1.
Phylogenetic tree (A) and alignment of partial amino acid sequences (B) of ParA and MinD homologues in various bacteria. Forty-three ParA and sixteen MinD homologues were found in databases by using the blast algorithm. Homologues of the E. coli MinD protein are shown when the blast score was over 65. The ParA homologues that belong to the chromosomal group are indicated in blue and those to the extrachromosomal group in pink. The MinD members are indicated in yellow. In the aligned sequences, conserved residues and conservative substitutions (V/I/L, T/S, D/E, N/Q, Y/F, R/K) are shaded in red if present in 48 or more sequences of 60 ParA/MinD homologues, in green if present in 34 or more sequences of 43 ParA homologues, and in orange if present in 13 or more sequences of 16 MinD homologues. Amino acid residues are indicated with the one-letter code. *, parA genes in the extrachromosomal group were located on chromosomes.