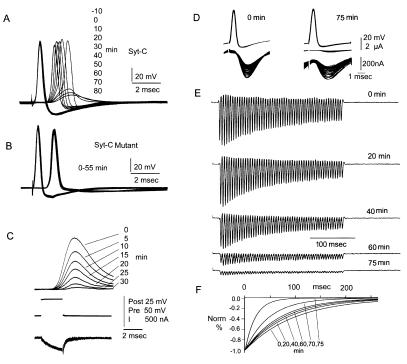
Figure 2.
Presynaptic injection of the Syt-C peptide reduces transmitter release in the squid giant synapse. (A) Pre- and postsynaptic recordings after Syt-C injection. (A) Reduction of postsynaptic potential without affecting the amplitude or duration of the presynaptic spike. Time after injection is indicated on the right. (B) Syt-CM peptide showed no reduction in postsynaptic potential amplitude. (C) Syt-C injection reduces transmitter release without affecting presynaptic calcium current at the preterminal. Top traces postsynaptic amplitude; Middle traces presynaptic voltage step; Lower traces presynaptic calcium current. For all records, time interval after injection is indicated in minutes (Right). (D) Kinetics of transmitter release reduction after Syt-C peptide injection. Presynaptic spike trains at 200 Hz generate a rapid PSC decrease within each train (Right). The amplitude of the PSC is reduced, and the rate of reduction is increased with time after injection (Left, at 75 min after injection). PSC were amplified 10× (Bottom). (E) Set of PSC produced by a train of stimuli at 200 Hz. (F) Plot of the time course for PSC amplitude against time for each set of spike trains. Note the increase rate of decline of PSC with time after injection.