Fig. 2.
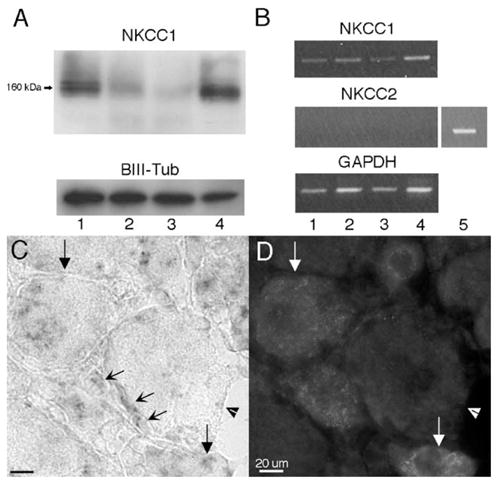
Assessment of NKCC1 protein and mRNA in dorsal root, DRG, sciatic nerve and spinal dorsal horn and NKCC1 mRNA expression in the DRG: (A) representative Western blots illustrating the presence of NKCC1 protein detected as a band at 160 kDa from dorsal root (1), DRG (2), sciatic nerve (3) and dorsal horn (4) protein homogenates (10 μg protein/lane). β-III tubulin was utilized as a loading control. (B) Representative RT-PCR illustrating the presence of NKCC1 mRNA in the dorsal root (1), DRG (2), sciatic nerve (3) and dorsal horn (4) and the absence of NKCC2. Kidney (5) RNA was utilized as a positive control for NKCC2. GAPDH mRNA was used as a loading control. (C) High magnification (100×) image of NKCC1 mRNA in the DRG and the corresponding CGRP IHC image (D). Downward arrows: NKCC1 mRNA- and CGRP-expressing neurons. Arrowheads: large diameter NKCC1 mRNA- and CGRP-negative neuron. Concave diagonal arrows: NKCC1 mRNA-expressing glial cells in the DRG. Many of these cells appeared to be satellite glial cells (SGCs) based on their location ensheathing the soma of neurons.
