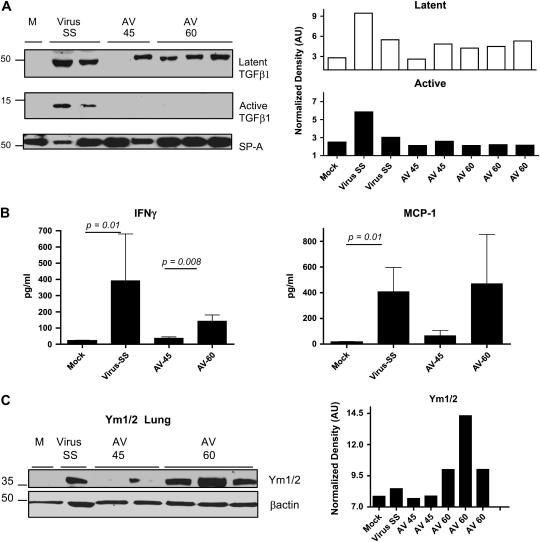
Figure 7.
Antiviral treatment in symptomatic mice fails to control alternative activation of macrophages. (A) Western blot analysis for the latent and active forms of TGF-β in bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) fluid samples collected on Day 120. Blot was stripped and reprobed with an anti-surfactant A (SP-A) antibody to normalize expression of latent (open columns) and active (solid columns) TGF-β. Decreased levels of active TGF-β were found in symptomatic infected mice treated with the antiviral agent. (B) IFN-γ and monocyte chemotactic protein (MCP)–1 levels were measured in BAL fluid from mock and MHV68-infected IFN-γR−/− mice after treatment with saline solution (SS) or antiviral, which was begun on Day 45 or 60 postinfection (AV-45 and AV-60, respectively). Levels of cytokines were determined in a multiplex bead immunoassay on Day 120. Shown are means and SEM. Number of mice: mock (n = 5); AV-45 (n = 5); virus SS (n = 6); AV-60 (n = 6). (C) Lung homogenate from mock and virus-infected mice treated with saline solution or antiviral were subjected to Western blot analysis for Ym1/2 proteins. Antiviral begun on Day 60 postinfection failed to lower levels of Ym proteins in the lungs. Blot was stripped and reprobed with an anti–β-actin antibody to normalize expression of Ym1/2.