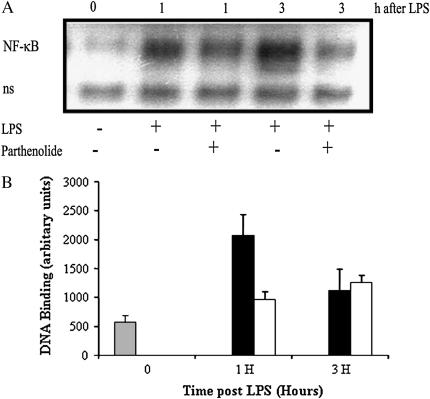
Figure 6.
Effect of in vivo treatment with parthenolide on the activation of NF-κB in the CF lung. Mice were pretreated with parthenolide 3 μg/g body weight or placebo 1 h before intratracheal LPS challenge. Mice underwent BAL and the lungs were perfused, removed at the indicated times, and nuclei were prepared and extracted for EMSA. (A) Representative autoradiograph of EMSA for activated NF-κB. 0 = mice not challenged with LPS. Results are shown for 1 and 3 h, with (+) and without (−) parthenolide. (B) Image analysis of activation of NF-κB determined by densitometry from two separate time course experiments (n = 5 mice in each time points and group). Mean ± SEM are shown. Parthenolide-treated mice (open bar) had significantly increased NF-κB activation at 1 h after LPS as compared with placebo group (solid bar) (P = 0.05). (“ns” in lower row is “non-specifically bound”.)