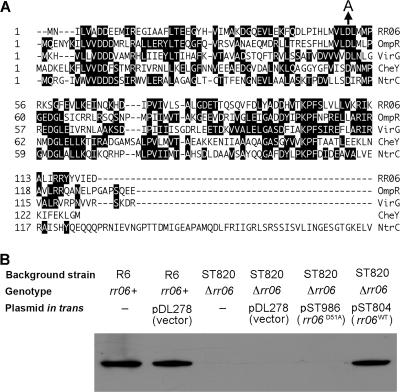
FIG. 5.
Functional impact of RR06 phosphorylation. A. Partial sequence alignment of RR06, OmpR (accession no. AAN82619), VirG (accession no. NP_059810), CheY (accession no. AAA23577), and NtrC (accession no. CAA59425) by the Clustal W method in the MegAlign program of DNASTAR Lasergene v6.1. Identical amino acids are shaded. Gaps were introduced for optimal alignment as indicated by dashed lines. Amino acid positions of each sequence are marked on the left side according to the relative distance from the first amino acid. Only the amino-terminal region of NtrC is shown. The D-to-A mutation at Asp-51 of RR06 is marked with an arrow. B. Restoration of CbpA expression in the rr06-null strain ST820 by genetic complementation with the wild-type rr06 or mutant rr06(D51A) allele. ST820 was transformed with either pDL278 (vector) or the plasmids harboring the wild-type (rr06WT, pST804) or mutant (rr06D51A, pST982) rr06. The resultant strains were used to detect CbpA by Western blotting as described for Fig. 4A. The wild-type strain R6 was also transformed with the empty vector as a negative control.