Figure 4. Dose-dependence of eosin inhibition on K+-dependent phosphatase activity.
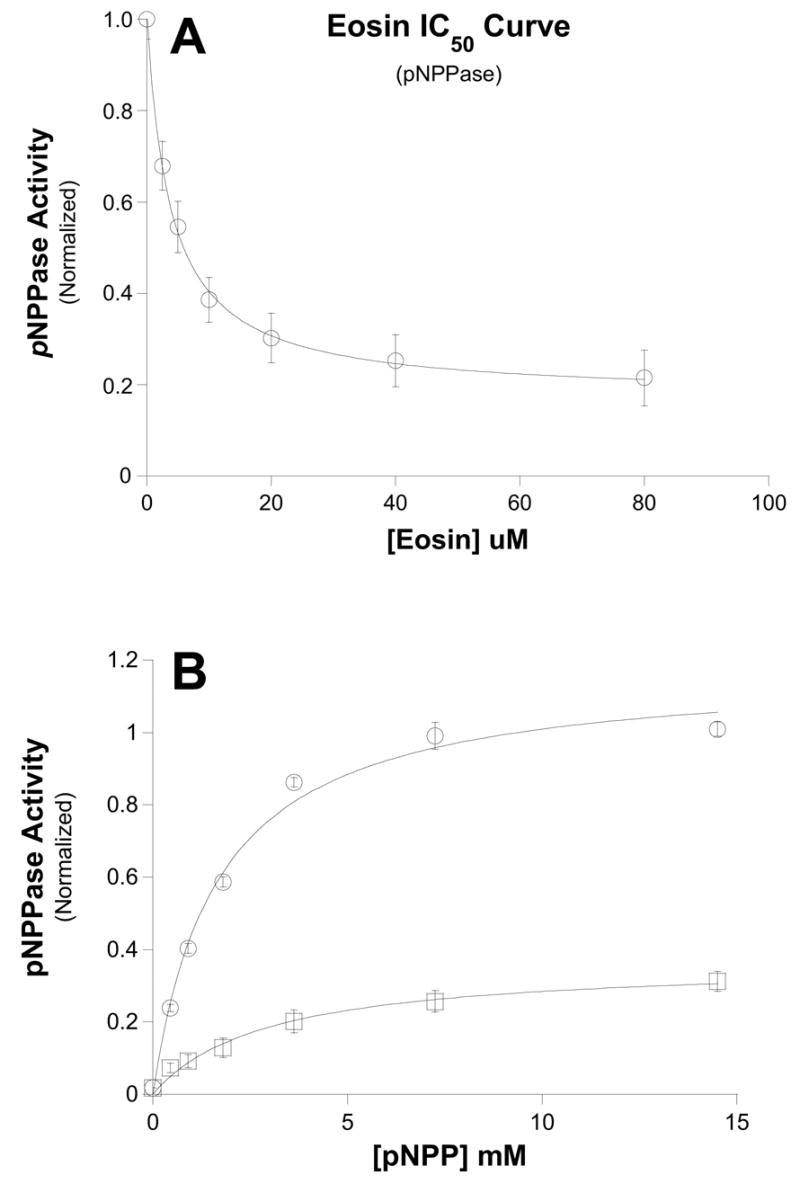
Ouabain-sensitive, K+-dependent pNPPase activity was measured in the presence of the indicated concentrations of eosin (see Methods). Data were fit to the same equation show in Fig. 1. Interestingly, the IC50 curve appears to plateau with a residual noneosin-sensitive 20% activity. The IC50 for eosin-sensitive component was 3.8 ± 0.23 μM. Data points are means and bars are standard error of six separate experiments. B.) pNPP dose-dependence of eosin inhibition. K+-dependent phosphatase activity was measured with increasing [pNPP] in the absence (○) and presence (□) of 25μM eosin. Data were fit to the Michaelis-Menten equation. Control Vmax = 1.17 ± 0.05; K1/2 = 1.65 ± 0.21 μM; 25 μM eosin Vmax = 0.38 ± 0.05; K1/2 = 2.91 ± 0.54 μM. These data suggest that eosin does not compete with pNPP. Data points are means and bars are standard error of three separate experiments.
