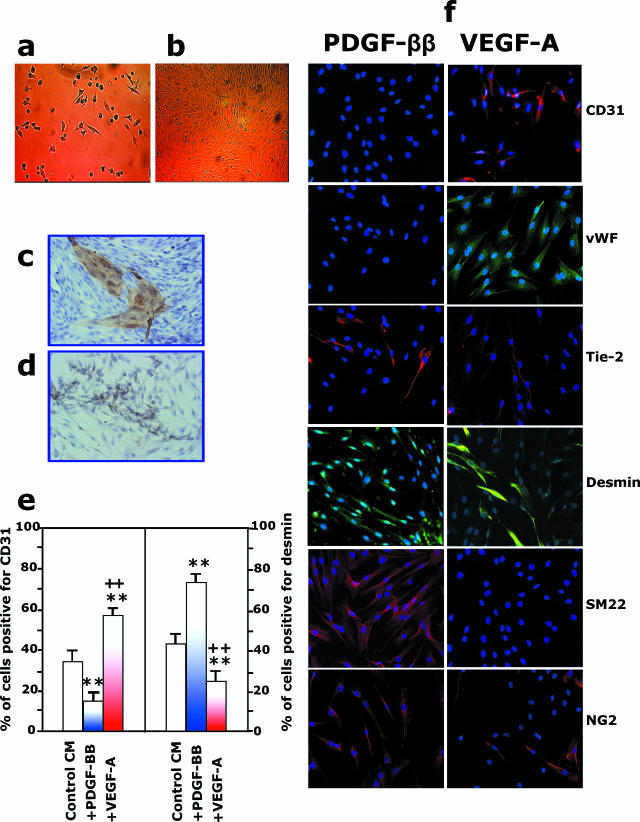
Figure 2.
CD133+CD34+KDR+ cells derived from hFA differentiate into vascular endothelial and mural cells. a and b: Freshly immunoselected CD133+CD34+KDR+ cells seeded on collagen type I-plus fibronectin-coated dishes were cultured under differentiated culture medium EBM-GM.16 a: A few hours after seeding, cells started to adhere. At 7 days of culture, the formation of mature EC colonies was observed, and at confluence, 10 to 14 days after seeding, mature ECs could be separated from the culture by using immunomagnetic beads coated with anti-CD31. The newly formed mature ECs could be grown in EBM-GM to obtain a typical endothelial monolayer in b. Magnification, ×10. The formation of EC colonies on confluent culture was also confirmed by immunoperoxidase staining with anti-CD31 antibody (c), whereas the presence of mural cells was shown by their immunoreactivity with anti-α-SMA antibody (d). e and f: Addition of PDGF-ββ or VEGF-A to EBM-GM enhanced the formation of mural and endothelial cells, respectively. Quantification is shown in e. **P < 0.01 versus control medium, ++P < 0.01 versus PDGF-ββ addition. f: Immunostaining for CD31, vWF, Tie-2, desmin, smooth muscle 22α, and NG2 of CD133+CD34+KDR+ cells 10 days on stimulation with PDGF-ββ or VEGF-A.