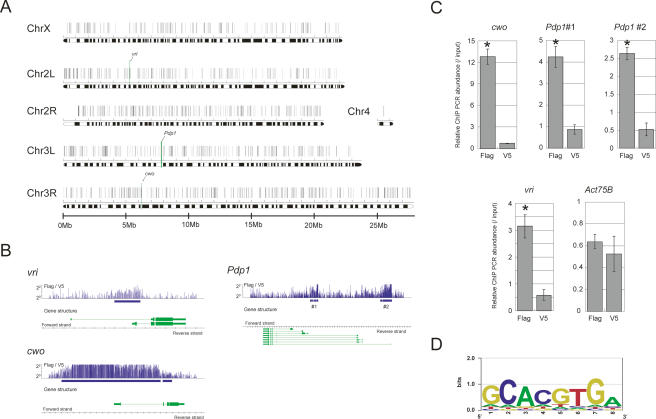
Figure 4.
CWO protein directly targets known clock genes. (A) Chromosomal view of potential CWO-binding sites (black vertical bar on each chromosome) identified by ChIP assay on a Drosophila genome tiling array. The locations of vri, Pdp1, and cwo are indicated as a green vertical bar. (B) Close view of potential cwo-binding sites on vri, Pdp1, and cwo genes. (Top panel) The fold changes between signal (Flag) and background (V5) were plotted for each probe with the potential binding sites (blue box). (Bottom panel) Gene structures are also indicated. We identified two independent binding sites in the Pdp1 promoter (Pdp1 #1 and #2). (C) Independent verification of ChIP experiments. The relative abundance of immunoprecipitated chromosome regions was measured using a Q-PCR assay. Input product (genomic DNA without ChIP) was used as an internal control. Act57B is used as a negative control. Error bars represent the SEM (n = 3). cwo, Pdp1, and vri promoters are significantly bound by CWO protein. (*) p < 0.05 in t-test. (D) Canonical E-box (CACGTG) recognized by CWO protein. The DNA sequence overrepresented in potential CWO-binding sites was identified by Weeder and drawn by EnoLOGOS.