Full text
PDF

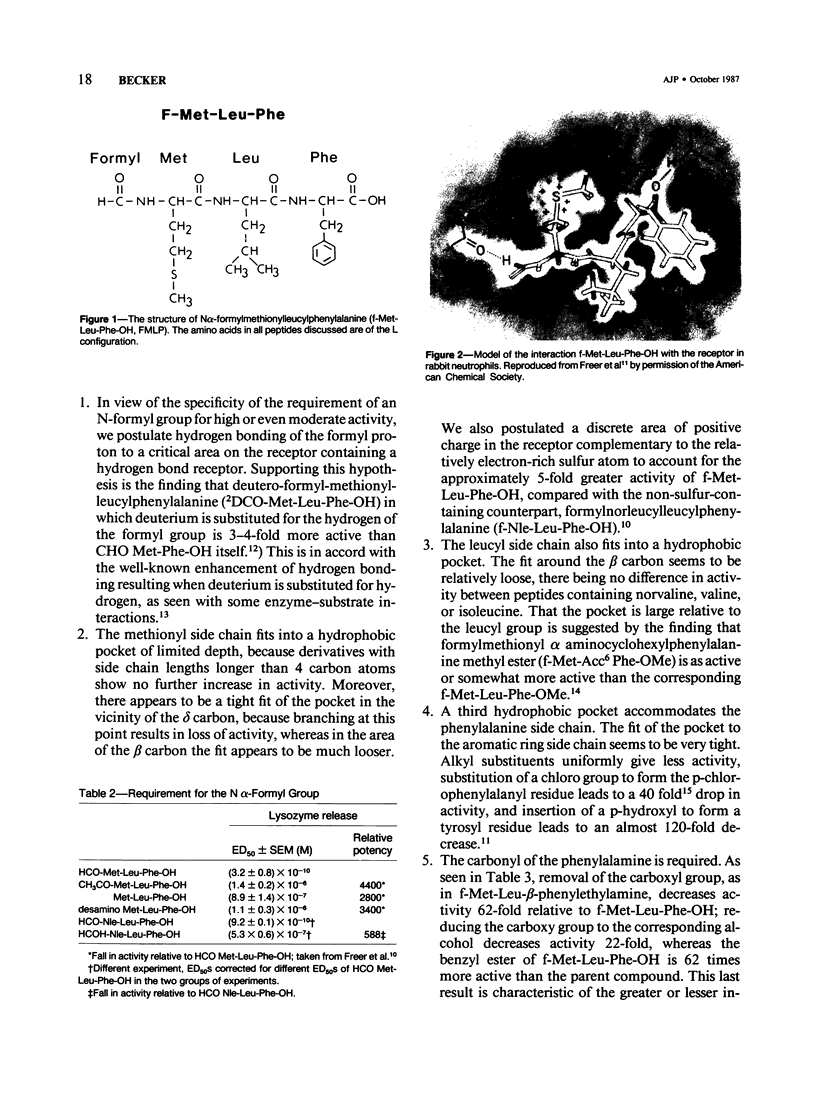






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arányi P. Deuterium isotope effects on the rates of steroid--glucocorticoid receptor interactions. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Jan 2;138(1):89–92. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb07885.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aswanikumar S., Corcoran B., Schiffmann E., Day A. R., Freer R. J., Showell H. J., Becker E. L. Demonstration of a receptor on rabbit neutrophils for chemotactic peptides. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Jan 24;74(2):810–817. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)90375-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrowman M. M., Cockcroft S., Gomperts B. D. Two roles for guanine nucleotides in the stimulus-secretion sequence of neutrophils. Nature. 1986 Feb 6;319(6053):504–507. doi: 10.1038/319504a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker E. L., Bleich H. E., Day A. R., Freer R. J., Glasel J. A., Visintainer J. Nuclear magnetic resonance conformational studies on the chemotactic tripeptide formyl-L-methionyl-L-leucyl-L-phenylalanine. A small beta sheet. Biochemistry. 1979 Oct 16;18(21):4656–4668. doi: 10.1021/bi00588a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker E. L., Kermode J. C., Naccache P. H., Yassin R., Marsh M. L., Munoz J. J., Sha'afi R. I. The inhibition of neutrophil granule enzyme secretion and chemotaxis by pertussis toxin. J Cell Biol. 1985 May;100(5):1641–1646. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.5.1641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker E. L. Leukocyte stimulation: receptor, membrane, and metabolic events. Introduction and summary. Fed Proc. 1986 Jun;45(7):2148–2150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bismara C., Bonora G. M., Toniolo C., Becker E. L., Freer R. J. Synthetic homo-oligomethionine chemoattractants. Conformation-activity study. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1985 Nov;26(5):482–492. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1985.tb01015.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boukili M. A., Bureau M., Lagente V., Lefort J., Lellouch-Tubiana A., Malanchère E., Vargaftig B. B. Pharmacological modulation of the effects of N-formyl-L-methionyl-L-leucyl-L-phenylalanine in guinea-pigs: involvement of the arachidonic acid cascade. Br J Pharmacol. 1986 Oct;89(2):349–359. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1986.tb10267.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burka J. F. Effects of compound 48/80 and formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine on isolated guinea pig airways. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1984;73(4):309–313. doi: 10.1159/000233490. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chenoweth D. E., Lane T. A., Rowe J. G., Hugli T. E. Quantitative comparisons of neutrophil chemotaxis in four animal species. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1980 Mar;15(3):525–535. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(80)90064-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Day A. R., Radding J. A., Freer R. J. Synthesis and binding characteristics of an intrinsically radiolabeled chemotactic acyl tripeptide. N alpha-Formyl--norleucyl--leucyl--phenylalanine. FEBS Lett. 1977 May 15;77(2):291–294. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80254-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edmundson A. B., Ely K. R. Binding of N-formylated chemotactic peptides in crystals of the Mcg light chain dimer: similarities with neutrophil receptors. Mol Immunol. 1985 Apr;22(4):463–475. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(85)90131-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falloon J., Malech H., Milligan G., Unson C., Kahn R., Goldsmith P., Spiegel A. Detection of the major pertussis toxin substrate of human leukocytes with antisera raised against synthetic peptides. FEBS Lett. 1986 Dec 15;209(2):352–356. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81141-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feltner D. E., Smith R. H., Marasco W. A. Characterization of the plasma membrane bound GTPase from rabbit neutrophils. I. Evidence for an Ni-like protein coupled to the formyl peptide, C5a, and leukotriene B4 chemotaxis receptors. J Immunol. 1986 Sep 15;137(6):1961–1970. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freer R. J., Day A. R., Muthukumaraswamy N., Pinon D., Wu A., Showell H. J., Becker E. L. Formyl peptide chemoattractants: a model of the receptor on rabbit neutrophils. Biochemistry. 1982 Jan 19;21(2):257–263. doi: 10.1021/bi00531a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freer R. J., Day A. R., Radding J. A., Schiffmann E., Aswanikumar S., Showell H. J., Becker E. L. Further studies on the structural requirements for synthetic peptide chemoattractants. Biochemistry. 1980 May 27;19(11):2404–2410. doi: 10.1021/bi00552a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gierschik P., Falloon J., Milligan G., Pines M., Gallin J. I., Spiegel A. Immunochemical evidence for a novel pertussis toxin substrate in human neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 15;261(17):8058–8062. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gnessi L., Ruff M. R., Fraioli F., Pert C. B. Demonstration of receptor-mediated chemotaxis by human spermatozoa. A novel quantitative bioassay. Exp Cell Res. 1985 Nov;161(1):219–230. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(85)90506-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray G. D., Knight K. A., Nelson R. D., Herron M. J. Chemotactic requirements of bovine leukocytes. Am J Vet Res. 1982 May;43(5):757–759. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray G. D., Ohlmann G. M., Morton D. R., Schaub R. G. Feline polymorphonuclear leukocytes respond chemotactically to leukotriene B4 and activated serum but not to F-Met-Leu-Phe. Agents Actions. 1986 Jun;18(3-4):401–406. doi: 10.1007/BF01965004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamel R., Ford-Hutchinson A. W., Lord A., Cirino M. Bronchoconstriction induced by N-formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine in the guinea pig; involvement of arachidonic acid metabolites. Prostaglandins. 1984 Jul;28(1):43–56. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(84)90112-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang C. K. Partial purification and characterization of formylpeptide receptor from rabbit peritoneal neutrophils. J Leukoc Biol. 1987 Jan;41(1):63–69. doi: 10.1002/jlb.41.1.63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyslop P. A., Oades Z. G., Jesaitis A. J., Painter R. G., Cochrane C. G., Sklar L. A. Evidence for N-formyl chemotactic peptide-stimulated GTPase activity in human neutrophil homogenates. FEBS Lett. 1984 Jan 23;166(1):165–169. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)80065-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iqbal M., Shivaji S., Vijayasarathy S., Balaram P. Synthetic peptides as chemoattractants for bull spermatozoa structure activity correlations. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Sep 16;96(1):235–242. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)91205-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koo C., Lefkowitz R. J., Snyderman R. Guanine nucleotides modulate the binding affinity of the oligopeptide chemoattractant receptor on human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Clin Invest. 1983 Sep;72(3):748–753. doi: 10.1172/JCI111045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lad P. M., Olson C. V., Grewal I. S. A step sensitive to pertussis toxin and phorbol ester in human neutrophils regulates chemotaxis and capping but not phagocytosis. FEBS Lett. 1986 May 5;200(1):91–96. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80517-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marasco W. A., Fantone J. C., Ward P. A. Spasmogenic activity of chemotactic N-formylated oligopeptides: identity of structure--function relationships for chemotactic and spasmogenic activities. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7470–7473. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marasco W. A., Phan S. H., Krutzsch H., Showell H. J., Feltner D. E., Nairn R., Becker E. L., Ward P. A. Purification and identification of formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine as the major peptide neutrophil chemotactic factor produced by Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 10;259(9):5430–5439. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marasco W. A., Showell H. J., Freer R. J., Becker E. L. Anti-f Met-Leu-Phe: similarities in fine specificity with the formyl peptide chemotaxis receptor of the neutrophil. J Immunol. 1982 Feb;128(2):956–962. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niedel J. Detergent solubilization of the formyl peptide chemotactic receptor. Strategy based on covalent affinity labeling. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 10;256(17):9295–9299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niedel J., Wilkinson S., Cuatrecasas P. Receptor-mediated uptake and degradation of 125I-chemotactic peptide by human neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 10;254(21):10700–10706. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okajima F., Ui M. ADP-ribosylation of the specific membrane protein by islet-activating protein, pertussis toxin, associated with inhibition of a chemotactic peptide-induced arachidonate release in neutrophils. A possible role of the toxin substrate in Ca2+-mobilizing biosignaling. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):13863–13871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redl H., Flynn P. J., Lamche H., Schiesser A., Schlag G., Hammerschmidt D. E. Aggregation, chemotaxis, and chemiluminescence of canine granulocytes. Studies utilizing improved cell preparation techniques. Inflammation. 1983 Mar;7(1):67–80. doi: 10.1007/BF00918009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiffmann E., Corcoran B. A., Wahl S. M. N-formylmethionyl peptides as chemoattractants for leucocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):1059–1062. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.1059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiffmann E., Showell H. V., Corcoran B. A., Ward P. A., Smith E., Becker E. L. The isolation and partial characterization of neutrophil chemotactic factors from Escherichia coli. J Immunol. 1975 Jun;114(6):1831–1837. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Showell H. J., Freer R. J., Zigmond S. H., Schiffmann E., Aswanikumar S., Corcoran B., Becker E. L. The structure-activity relations of synthetic peptides as chemotactic factors and inducers of lysosomal secretion for neutrophils. J Exp Med. 1976 May 1;143(5):1154–1169. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.5.1154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyderman R., Pike M. C. N-Formylmethionyl peptide receptors on equine leukocytes initiate secretion but not chemotaxis. Science. 1980 Jul 25;209(4455):493–495. doi: 10.1126/science.6248959. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spangrude G. J., Sacchi F., Hill H. R., Van Epps D. E., Daynes R. A. Inhibition of lymphocyte and neutrophil chemotaxis by pertussis toxin. J Immunol. 1985 Dec;135(6):4135–4143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stryer L., Bourne H. R. G proteins: a family of signal transducers. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1986;2:391–419. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.02.110186.002135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sukumar M., Raj P. A., Balaram P., Becker E. L. A highly active chemotactic peptide analog incorporating the unusual residue 1-aminocyclohexanecarboxylic acid at position 2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Apr 16;128(1):339–344. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91684-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toniolo C., Bonora G. M., Showell H., Freer R. J., Becker E. L. Structural requirements for formyl homooligopeptide chemoattractants. Biochemistry. 1984 Feb 14;23(4):698–704. doi: 10.1021/bi00299a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verghese M., Uhing R. J., Snyderman R. A pertussis/choleratoxin-sensitive N protein may mediate chemoattractant receptor signal transduction. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Jul 31;138(2):887–894. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80579-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward P. A., Lepow I. H., Newman L. J. Bacterial factors chemotactic for polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Am J Pathol. 1968 Apr;52(4):725–736. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams L. T., Snyderman R., Pike M. C., Lefkowitz R. J. Specific receptor sites for chemotactic peptides on human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):1204–1208. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.1204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]