Abstract
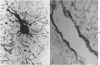
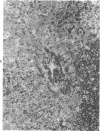
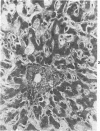
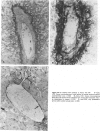
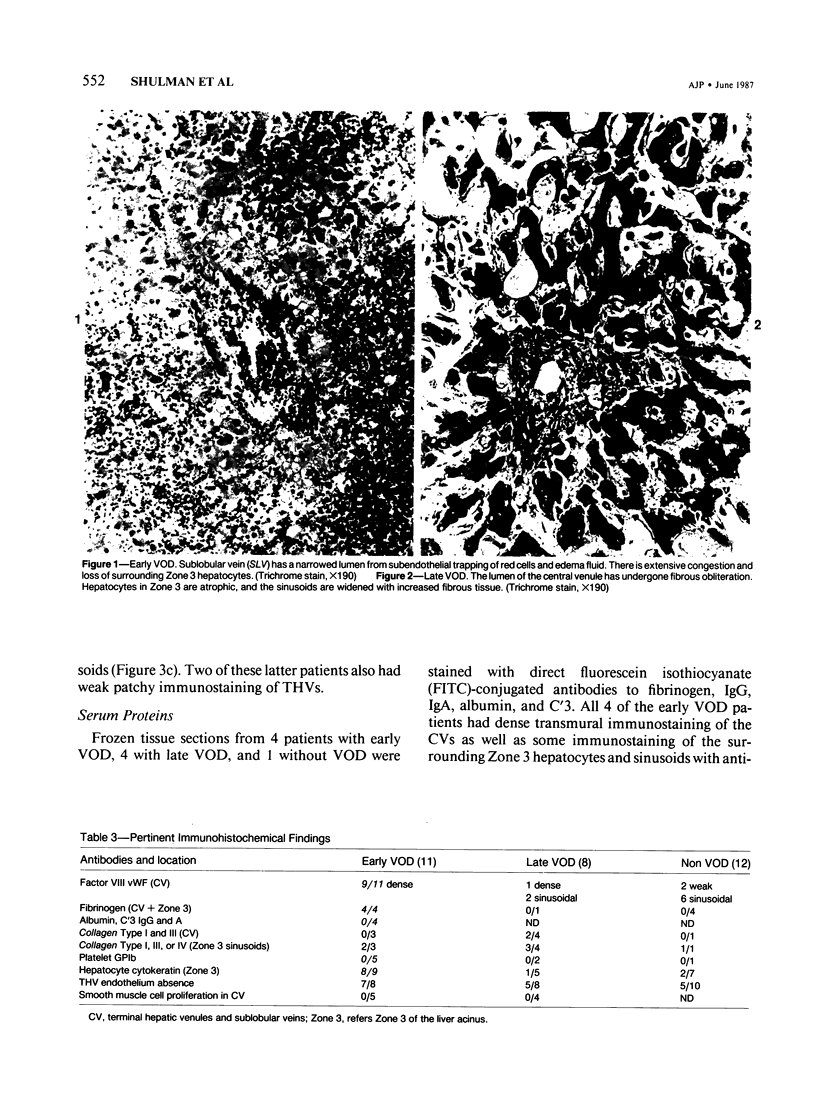
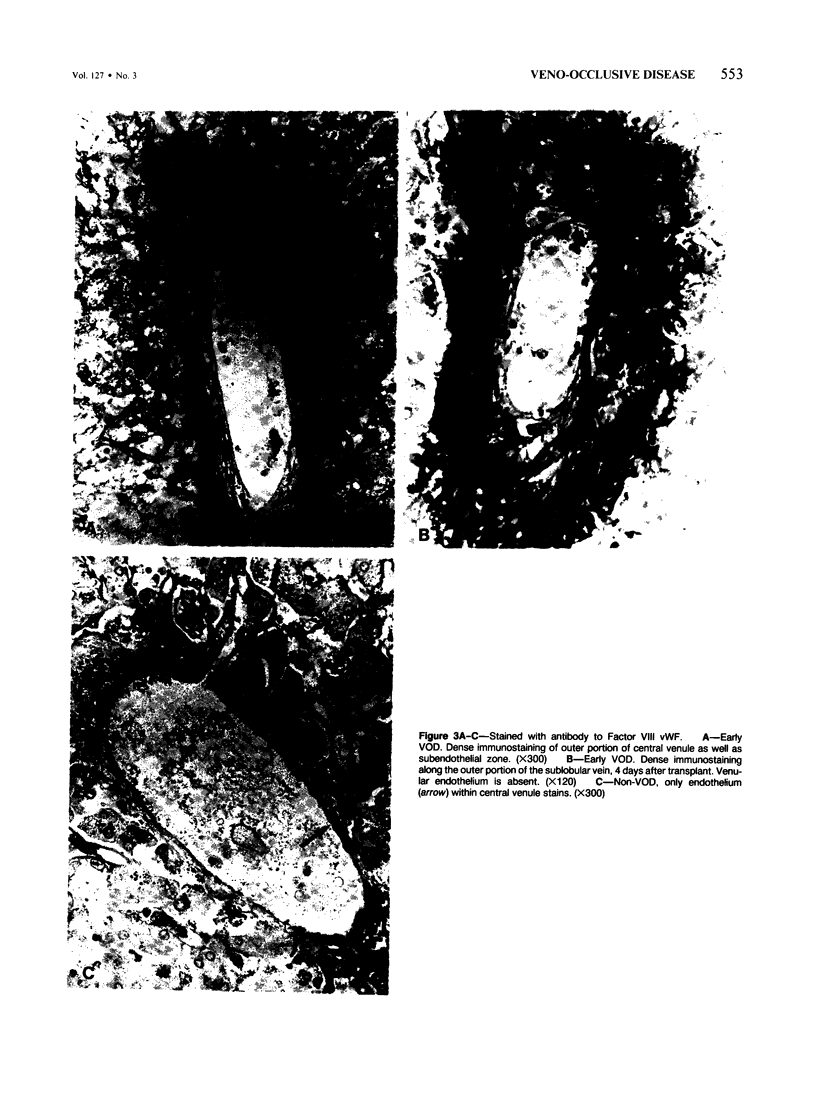
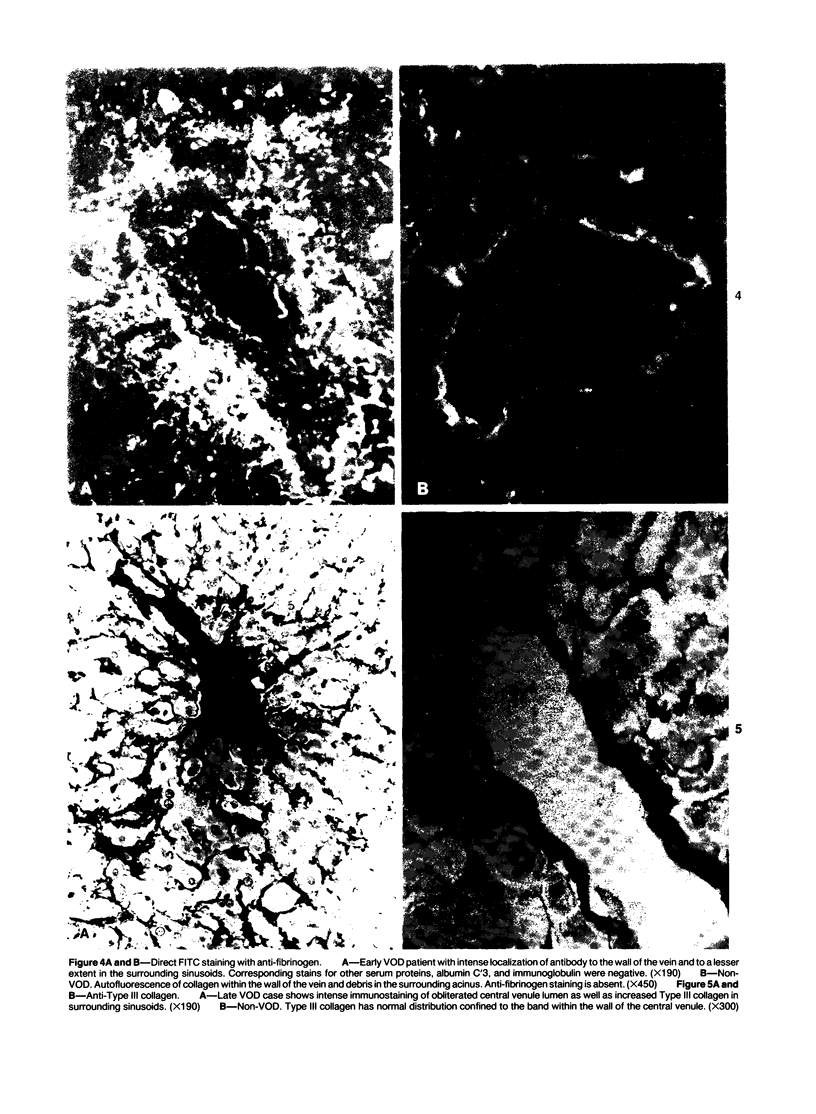
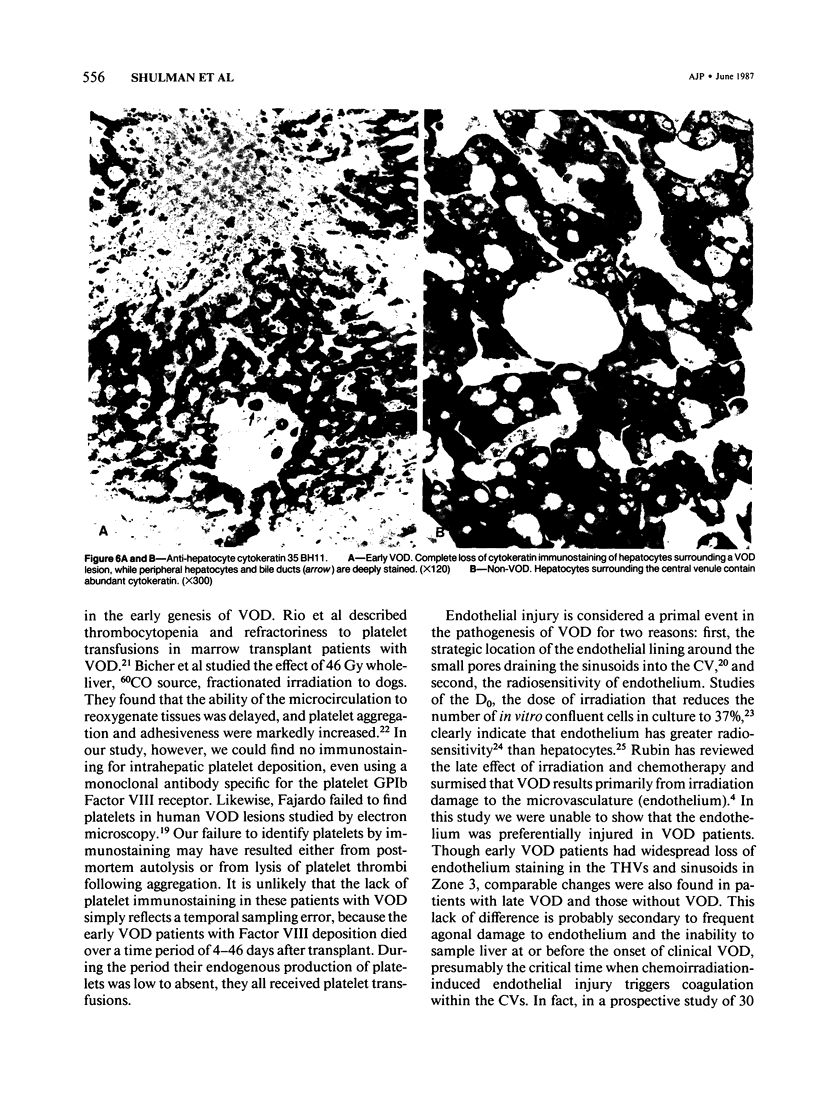
The authors immunostained autopsy liver tissue from 31 marrow transplant recipients, 19 with hepatic veno-occlusive disease (VOD) and 12 without VOD. A panel of monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies was used to characterize the materials within the occluded venous lesions and to define the location and types of injured cells. Most patients with early VOD (survival less than 50 days, n = 11) had dense periadventitial and intramural immunostaining of terminal hepatic and sublobular central venules (CV) with anti-Factor VIII (9/11) and anti-fibrinogen (4/4) but had no immunostaining with antibody to platelet GPIb. Early VOD patients also had marked loss of Zone 3 hepatocyte cytokeratin (8/9) versus late VOD (1/5) or non-VOD (2/7). Patients with late VOD lesions (n = 8, survival greater than 50 days) had increased collagen within occluded VOD lesions. Type III much greater than Type I, and increased sinusoidal collagens Types I, III, and IV. These studies and other data suggest the following events in the genesis of VOD. Initial injury to endothelium of CV and/or sinusoids and possibly also to Zone 3 hepatocytes triggers the coagulation cascade in the periadventitial zone of CV. The late sequela, collagenous CV occlusion, results from activated mural myofibroblasts and/or embolized Ito cells and hepatocytes.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bicher H. I., Dalrymple G. V., Ashbrook D., Smith R., Harris D. Effect of ionizing radiation on liver microcirculation and oxygenation. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1976;75:497–503. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-3273-2_59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cahn J. Y., Flesch M., Plouvier E., Hervé P., Rozenbaum A. Maladie veino-occlusive du foie et autogreffe de moelle osseuse. Rôle préventif de l'héparine? Nouv Rev Fr Hematol. 1985;27(1):27–28. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clement B., Grimaud J. A., Campion J. P., Deugnier Y., Guillouzo A. Cell types involved in collagen and fibronectin production in normal and fibrotic human liver. Hepatology. 1986 Mar-Apr;6(2):225–234. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840060212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clouse L. H., Comp P. C. The regulation of hemostasis: the protein C system. N Engl J Med. 1986 May 15;314(20):1298–1304. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198605153142006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deeg H. J., Shulman H. M., Schmidt E., Yee G. C., Thomas E. D., Storb R. Marrow graft rejection and veno-occlusive disease of the liver in patients with aplastic anemia conditioned with cyclophosphamide and cyclosporine. Transplantation. 1986 Nov;42(5):497–501. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198611000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emeis J. J., Kooistra T. Interleukin 1 and lipopolysaccharide induce an inhibitor of tissue-type plasminogen activator in vivo and in cultured endothelial cells. J Exp Med. 1986 May 1;163(5):1260–1266. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.5.1260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fajardo L. F., Colby T. V. Pathogenesis of veno-occlusive liver disease after radiation. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1980 Nov;104(11):584–588. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein L. C., Corey L., McDougall J. K., Tolentino E., Nowinski R. C. Monoclonal antibodies to herpes simplex viruses: use in antigenic typing and rapid diagnosis. J Infect Dis. 1983 May;147(5):829–837. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.5.829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein L. C., McDougall J., Hackman R., Meyers J. D., Thomas E. D., Nowinski R. C. Monoclonal antibodies to cytomegalovirus: rapid identification of clinical isolates and preliminary use in diagnosis of cytomegalovirus pneumonia. Infect Immun. 1982 Oct;38(1):273–281. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.1.273-281.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gown A. M., Vogel A. M. Monoclonal antibodies to human intermediate filament proteins. II. Distribution of filament proteins in normal human tissues. Am J Pathol. 1984 Feb;114(2):309–321. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gown A. M., Vogel A. M. Monoclonal antibodies to intermediate filament proteins of human cells: unique and cross-reacting antibodies. J Cell Biol. 1982 Nov;95(2 Pt 1):414–424. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.2.414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irle C., Deeg H. J., Buckner C. D., Kennedy M., Clift R., Storb R., Appelbaum F. R., Beatty P., Bensinger W., Doney K. Marrow transplantation for leukemia following fractionated total body irradiation. A comparative trial of methotrexate and cyclosporine. Leuk Res. 1985;9(10):1255–1261. doi: 10.1016/0145-2126(85)90153-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jirtle R. L., Michalopoulos G., McLain J. R., Crowley J. Transplantation system for determining the clonogenic survival of parenchymal hepatocytes exposed to ionizing radiation. Cancer Res. 1981 Sep;41(9 Pt 1):3512–3518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson L. K., Longenecker J. P., Fajardo L. F. Differential radiation response of cultured endothelial cells and smooth myocytes. Anal Quant Cytol. 1982 Sep;4(3):188–198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunicki T. J., Nugent D. J., Piotrowicz R. S., Lai C. S. Covalent attachment of sulfhydryl-specific, electron spin resonance spin-labels to Fab' fragments of murine monoclonal antibodies that recognize human platelet membrane glycoproteins. Development of membrane protein specific spin probes. Biochemistry. 1986 Sep 9;25(18):4979–4983. doi: 10.1021/bi00366a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lightdale C. J., Wasser J., Coleman M., Brower M., Tefft M., Pasmantier M. Anticoagulation and high dose liver radiation: a preliminary report. Cancer. 1979 Jan;43(1):174–181. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197901)43:1<174::aid-cncr2820430126>3.0.co;2-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludwig J., Axelsen R. Drug effects on the liver. An updated tabular compilation of drugs and drug-related hepatic diseases. Dig Dis Sci. 1983 Jul;28(7):651–666. doi: 10.1007/BF01299927. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCord J. M. Oxygen-derived free radicals in postischemic tissue injury. N Engl J Med. 1985 Jan 17;312(3):159–163. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198501173120305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald G. B., Sharma P., Matthews D. E., Shulman H. M., Thomas E. D. The clinical course of 53 patients with venocclusive disease of the liver after marrow transplantation. Transplantation. 1985 Jun;39(6):603–608. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198506000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald G. B., Sharma P., Matthews D. E., Shulman H. M., Thomas E. D. Venocclusive disease of the liver after bone marrow transplantation: diagnosis, incidence, and predisposing factors. Hepatology. 1984 Jan-Feb;4(1):116–122. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840040121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morel-Maroger Striker L., Killen P. D., Chi E., Striker G. E. The composition of glomerulosclerosis. I. Studies in focal sclerosis, crescentic glomerulonephritis, and membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis. Lab Invest. 1984 Aug;51(2):181–192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nawroth P. P., Stern D. M. Modulation of endothelial cell hemostatic properties by tumor necrosis factor. J Exp Med. 1986 Mar 1;163(3):740–745. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.3.740. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa K., Suzuki J., Narasaki M., Mori M. Healing of focal injury in the rat liver. Am J Pathol. 1985 Apr;119(1):158–167. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rio B., Andreu G., Nicod A., Arrago J. P., Dutrillaux F., Samama M., Zittoun R. Thrombocytopenia in venocclusive disease after bone marrow transplantation or chemotherapy. Blood. 1986 Jun;67(6):1773–1776. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowland F. N., Donovan M. J., Picciano P. T., Wilner G. D., Kreutzer D. L. Fibrin-mediated vascular injury. Identification of fibrin peptides that mediate endothelial cell retraction. Am J Pathol. 1984 Dec;117(3):418–428. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin P. The Franz Buschke lecture: late effects of chemotherapy and radiation therapy: a new hypothesis. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1984 Jan;10(1):5–34. doi: 10.1016/0360-3016(84)90408-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shulman H. M., McDonald G. B., Matthews D., Doney K. C., Kopecky K. J., Gauvreau J. M., Thomas E. D. An analysis of hepatic venocclusive disease and centrilobular hepatic degeneration following bone marrow transplantation. Gastroenterology. 1980 Dec;79(6):1178–1191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern D. M., Carpenter B., Nawroth P. P. Endothelium and the regulation of coagulation. Pathol Immunopathol Res. 1986;5(1):29–36. doi: 10.1159/000157001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storb R., Weiden P. L., Prentice R., Buckner C. D., Clift R. A., Einstein A. B., Fefer A., Johnson F. L., Lerner K. G., Neiman P. E. Aplastic anemia (AA) treated by allogeneic marrow transplantation: the Seattle experience. Transplant Proc. 1977 Mar;9(1):181–185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan K. M. Acute and chronic graft-versus-host disease in man. Int J Cell Cloning. 1986;4 (Suppl 1):42–93. doi: 10.1002/stem.5530040710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas E. D., Buckner C. D., Banaji M., Clift R. A., Fefer A., Flournoy N., Goodell B. W., Hickman R. O., Lerner K. G., Neiman P. E. One hundred patients with acute leukemia treated by chemotherapy, total body irradiation, and allogeneic marrow transplantation. Blood. 1977 Apr;49(4):511–533. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukada T., Tippens D., Gordon D., Ross R., Gown A. M. HHF35, a muscle-actin-specific monoclonal antibody. I. Immunocytochemical and biochemical characterization. Am J Pathol. 1987 Jan;126(1):51–60. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]