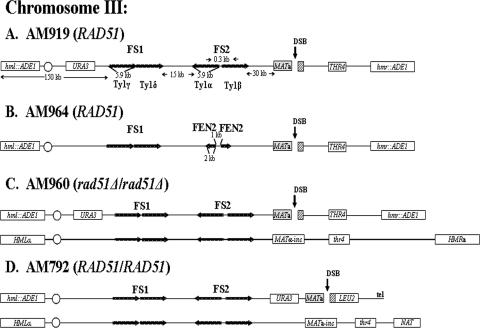
FIG. 1.
Arrangement of chromosome III markers in strains used to study effect of inverted repeats on DSB repair. (A) RAD51 haploid strain AM919. A DSB (black vertical arrow) is induced at MATa by a galactose-inducible HO gene. HML and HMR are replaced by ADE1. URA3 is inserted 133 kb from the left telomere, about 67 kb proximal to MATa. FS2 consists of two Ty1 elements (labeled Ty1α and Ty1β) in inverted orientation (24) and located 30 kb proximal to MAT. FS1 consists of two Ty1 elements (labeled Ty1γ and Ty1δ) in direct orientation located 57 kb centromere proximal to MATa. (B) RAD51 haploid strain AM964. This strain is similar to AM919 but with an inverted repeat of FEN2 replacing FS2. The distance between the two inverted copies of FEN2 is 1 kb. (C) rad51Δ/rad51Δ diploid strain AM960. In this strain, one copy of chromosome III (shown at the top) is the same as the chromosome in AM919. The other homologue contains MATα-inc, which cannot be cut by HO, and also has a mutant copy of the thr4 gene. This chromosome is about 20 kb longer than the homologue from AM919. (D) RAD51 diploid strain AM792. In this strain, the MATa-containing chromosome is truncated by insertion of the LEU2 gene fused to telomere (tel) sequences (29). The other homologue is similar to that of AM960, except that the HMR gene is replaced by the NAT (nourseothricin [Clonat] resistance) gene.