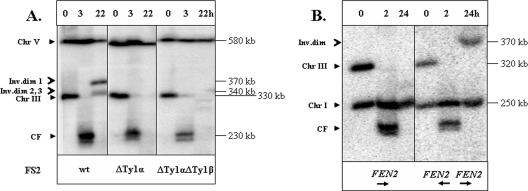
FIG. 2.
Interaction between inverted Ty1 elements leads to chromosome rearrangements. In this figure, the repair of DSBs in AM919 and related RAD51 strains was examined by PFGE. (A) Formation of chromosome (Chr) rearrangements depends on the presence of an intact FS2. DNA was prepared for PFGE at intervals (0, 3, and 22 h) after the induction of a DSB at MATa in the RAD51 haploid strains AM919, AM903 (ΔTy1α), and AM936 (ΔTy1α ΔTy1β). Southern blots were probed with URA3, which hybridizes with its normal locus on chromosome V and to a URA3 insertion on chromosome III (Fig. 1A). In AM919, two repair products were detected, one of about 370 kb (inverted dimer [Inv.dim] 1) and another of 340 kb. The smaller product was shown subsequently to represent two products of similar size (inverted dimers 2 and 3). The fragment labeled CF is the chromosome fragment resulting from deletion of the sequences centromere distal to the HO cleavage site. An additional CF band, observed 3 h after the addition of galactose, corresponds to the processed (partially single-stranded) form of cut fragment (K. VanHulle and A. Malkova, unpublished observation). (B) Formation of chromosome rearrangements is stimulated by an inverted repeat of the FEN2 gene. Experiments similar to those described for panel A were performed with the haploid strains AM915 (containing a deletion of FS2) and AM964 (containing an inverted repeat of FEN2 replacing FS2). Southern blots were probed with ADE1. A repair product of approximately 370 kb was observed in AM964 but not in AM915. wt, wild type.