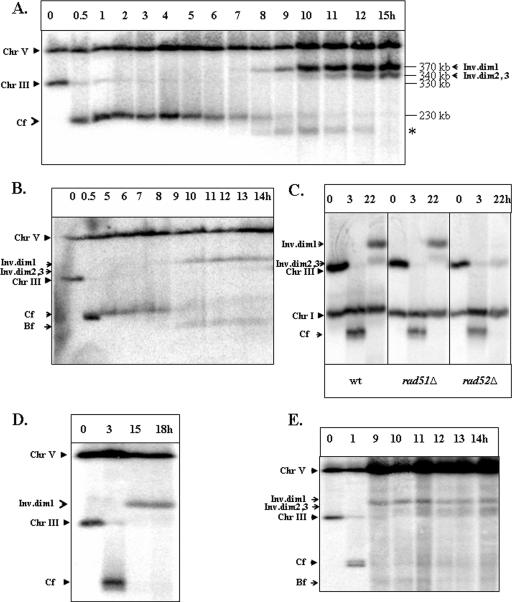
FIG. 5.
Kinetics and genetic requirements of Ty-mediated formation of inverted dimers. (A) Kinetics of formation of inverted dimers in AM919. DNA was prepared at intervals after the induction of a DSB at MATa in the RAD51 haploid strain AM919. Nocodazole was added 2 h following the addition of galactose. Southern blots were probed with URA3, which hybridizes to chromosome (Chr) V (its native locus) and to URA3 inserted about 15 kb from CEN3. The repair products (inverted dimers [Inv.dim] 1, 2, and 3) are indicated. Repair products of the same size were also observed after probing the same blots with an ADE1-specific probe located at the left end of chromosome III (data not shown). The nature of the band marked with asterisk is yet to be identified. (B) An experiment similar to the one shown in panel A was performed using AM919 cells that had not been treated with nocodazole. (C) Genetic requirements for formation of inverted dicentric dimers in haploid strains. The formation of inverted dimers was compared in AM919 (wild-type [wt]), EI517 (rad52Δ), and YLS73 (rad51Δ) strains arrested with nocodazole. Southern blots were probed with ADE1, which hybridized to ADE1 inserted at HML and HMR, and to its native locus on chromosome I. Dimer formation is independent of Rad51p but dependent on Rad52p. (D) Formation of inverted dimers in the rad51Δ/rad51Δ diploid strain AM960 treated with nocodazole. DNA was prepared for PFGE at intervals after the induction of DSBs at MATa in AM960 cells (Fig. 1C) arrested with nocodazole. Southern blots were hybridized to the URA3-specific probe. (E) Formation of inverted dimers in the rad51Δ/rad51Δ diploid strain AM960 that was not treated with nocodazole. DNA was prepared at intervals after induction of DSBs in AM960 cells that were not treated with nocodazole. Bf indicates DNA fragments that are likely to reflect breakage of dicentrics; Cf indicates chromosome fragments resulting from deletion of the sequences centromere distal to the HO cleavage site.