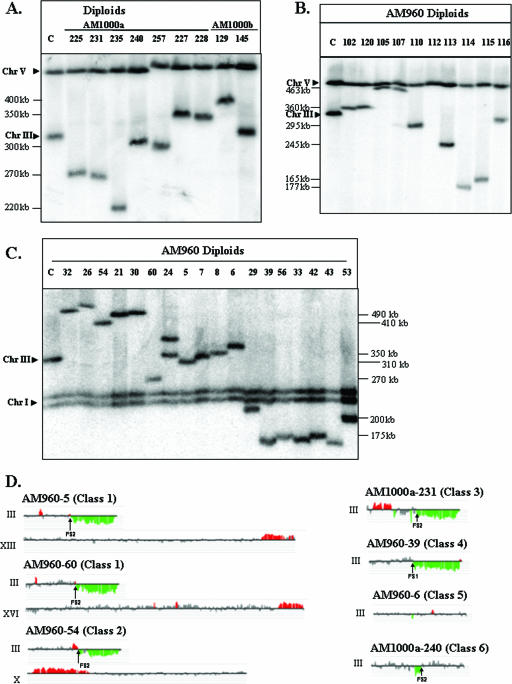
FIG. 6.
Chromosome rearrangements in strains with HO-induced DSBs. (A) Chromosome (Chr) alterations in derivatives of the RAD51 diploid strains AM1000a and AM1000b. DSBs were induced in the nocodazole-arrested RAD51 haploid AM919. The nocodazole was removed, and the haploids were mated to a RAD51 strain of the opposite mating type. We performed PFGE analysis of several independent diploids that were phenotypically Ade+ Thr− and expressed MATα information. The chromosomal DNA was analyzed with the URA3 probe (which hybridizes to both chromosomes III and V), although similar results were obtained with the ADE1-specific probe (data not shown). In many of the strains, the repair products were different in size from the normal-length chromosome IIIs, indicating a chromosome rearrangement. (B) Chromosome alterations in nocodazole-treated derivatives of the rad51 diploid strain AM960. DSBs were induced in the nocodazole-arrested rad51Δ diploid strain AM960. The nocodazole was removed, the cells were plated on YEP-plus-galactose medium, and the survivors were examined by PFGE. The chromosome III with the HO site was detected using URA3 as the hybridization probe, although similar results were obtained with the ADE1 probe (data not shown). The majority of the repair products were different in size from the two “normal” chromosome IIIs in AM960 (330 and 350 kb). (C) Chromosome alterations in derivatives of the rad51Δ diploid strain AM960 that were not treated with nocodazole. DSBs were induced in AM960 by plating on a galactose-containing medium, and we examined the consequences of these breaks in the surviving cells by PFGE. The chromosome III with the HO site was detected using ADE1 as the hybridization probe, although similar results were obtained with the URA3 probe (data not shown). The majority of the repair products were different in size from the two “normal” chromosome IIIs in AM960 (330 and 350 kb). The lanes labeled “C” in panels A, B, and C contained DNA from AM960 cells in which the HO site was not cleaved. (D) Genomic microarray analysis of chromosomal rearrangements. We depict gene dosages (CGH Miner format) for chromosomes in strains representing various classes of repair outcomes (see Table S1 in the supplemental material for details). Only chromosome III and rearranged chromosomes (containing chromosomal regions with changed gene dosage) are shown. Genomic DNA was isolated from strains with potential chromosome rearrangements and labeled with a Cy5-labeled fluorescent nucleotide; DNA from a reference strain (AM960) was labeled with Cy3 nucleotide. The two samples were mixed and hybridized to DNA microarrays that contained all yeast genes. Green indicates approximately twofold less DNA in the experimental strain relative to that in the control, and red indicates about 1.5-fold more DNA in the experimental strain. Small regions of red or green color (less than three open reading frames) were not considered significant. Also, regions of red or green color that were disrupted by gray-colored regions were not considered significant.