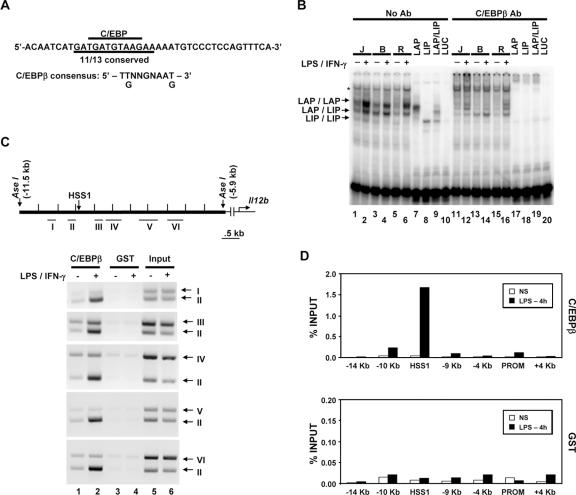
FIG. 8.
C/EBPβ binds the endogenous HSS1 enhancer. (A) The DNA sequence of the probe used for gel shift assays is shown, along with the C/EBP consensus recognition sequence. (B) Gel shift (lanes 1 to 10) and antibody (Ab) supershift (lanes 11 to 20) assays were performed as described in the legend to Fig. 6. Nuclear extracts from J774 (J), B6.129/J2 (B), and RAW264.7 (R) cells were examined, as well as in vitro-translated LAP (C/EBPβ large isoform; lanes 7 and 17), LIP (C/EBPβ small isoform; lanes 8 and 18), and cotranslated LAP and LIP (LAP/LIP) (lanes 9 and 19). In vitro-translated luciferase (LUC) (lanes 10 and 20) was tested as a negative control. The positions of protein-DNA complexes corresponding to LAP homodimers, LAP/LIP heterodimers, and LIP homodimers are indicated. A protein-DNA complex that does not interact with C/EBPβ antibodies is also apparent (*). (C) The Il12b genomic region examined for C/EBPβ binding by semiquantitative ChIP is shown. The locations of DNA fragments amplified by PCR (fragments I through VI) are indicated. The binding of C/EBPβ to the endogenous Il12b locus was monitored by ChIP using C/EBPβ or GST antibodies and chromatin samples prepared from peritoneal macrophages. Semiquantitative PCR was used to analyze the DNA fragments present in the immunoprecipitates. (D) ChIP experiments were performed with real-time PCR as described in the legend to Fig. 6, using chromatin prepared from bone marrow-derived macrophages. Similar results were obtained in a second independent experiment (not shown).