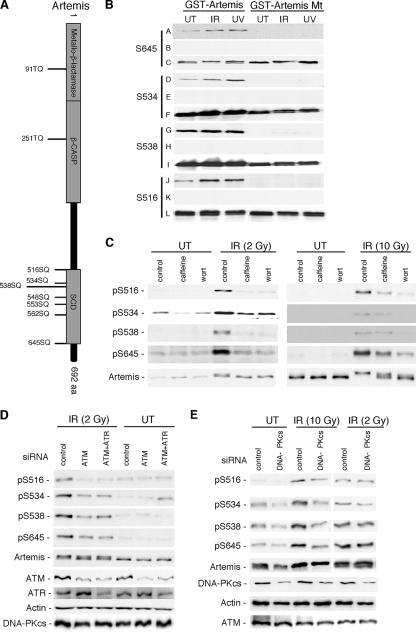
FIG. 1.
The role of ATM and DNA-PK in the phosphorylation of Artemis at specific SQ sites after IR treatment is dose dependent. (A) Schematic of Artemis showing (S/T)Q motifs conserved between human and mouse proteins. (B) Specificity of Artemis phospho-specific peptide antibodies to pS516, pS534, pS538, and pS645 as shown by immunoblot analysis. GST fusions of wild-type and the indicated Artemis S-to-A mutants (GST-Artemis mt) were stably expressed in HEK293 cells and exposed to either IR or UV. Rows A, D, G, and J show the signal detected from wild-type and mutant Artemis using the phospho-specific antibodies; rows B, E, H, and K show the lack of signal when the phospho-specific antibodies were preincubated with the appropriate phospho-peptide; and rows C, F, I, and L were probed with an Artemis polyclonal antibody. (C) Phospho-specific antibodies were used to probe the modification of Artemis at either low-dose (2 Gy) or high-dose (10 Gy) IR in the presence or absence of caffeine or wortmannin (wort). (D) Cells were depleted of ATM or ATM and ATR by siRNA treatment, and lysates were probed with the indicated antibodies. (E) Cells were depleted of DNA-PKcs by siRNA treatment and exposed to either low-dose or high-dose IR. Cell lysates were subsequently probed with the indicated antibodies. UT, untreated cells.