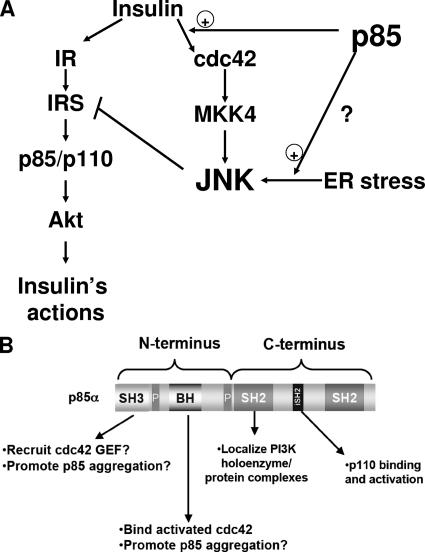
FIG. 8.
Molecular mechanisms of JNK activation by p85. (A) Schematic depiction of the role that p85 plays in activating JNK. The full-length p85 regulatory subunit potentiates the activation of JNK through the insulin/cdc42/MKK4 pathway and also facilitates the activation of JNK via the ER stress pathway. Activation of JNK through either pathway results in negative feedback on the insulin signaling pathway. Thus, the loss of p85 improves insulin sensitivity, in part by diminishing this JNK-mediated negative regulation. (B) Schematic of the structural features of the p85 regulatory subunit of PI3K showing how they may impact insulin action. The N terminus contains an SH3 domain, which may mediate intermolecular interactions with possible cdc42 guanine nucleotide exchange factors, while the BH domain binds activated cdc42. The SH2 domains in the C terminus are critical for proper function and localization of PI3K and may also mediate the recruitment of p85α to various cellular complexes. The proline-rich domains (P) are diagrammed, but we have not investigated the roles of these domains in p85α function.