FIG. 5.
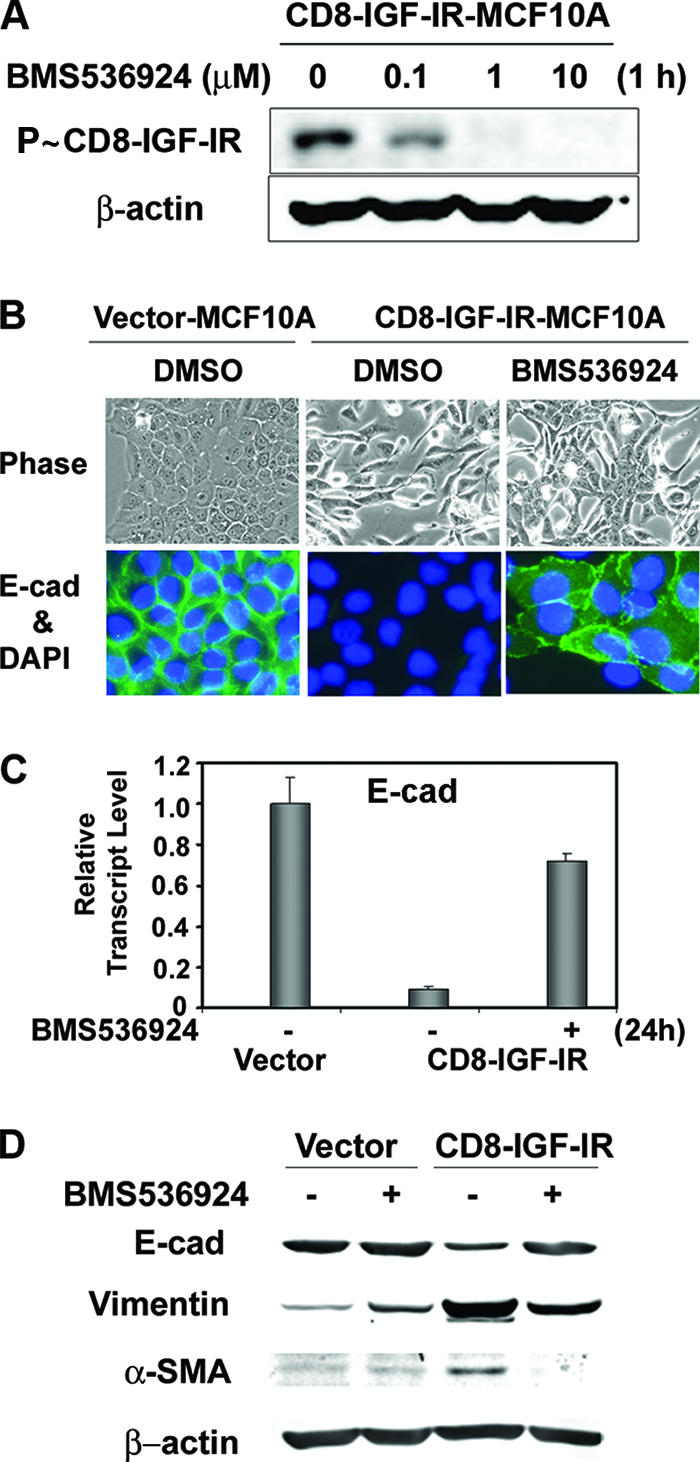
Blocking of constitutive IGF-IR activation by a new small-molecule inhibitor of IGF-IR, BMS-536924, partially reversed the mesenchyme-like morphological changes and the downregulation of E-cadherin levels. (A) CD8-IGF-IR-MCF10A cells were incubated with the indicated concentration of BMS-536924 for 1 h after 16 h of serum starvation, and the phosphorylation of CD8-IGF-IR was analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-P∼IGF-IR antibody. β-Actin was used as a loading control. (B) Vector-MCF10A and CD8-IGF-IR-MCF10A cells were incubated with or without 1 μM BMS-536924 for 24 h and were either visualized by phase-contrast microscopy at ×20 magnification (upper panels) or stained with E-cadherin (E-cad) (×40 magnification; green) (lower panels). The nuclei were stained with 4′,6′-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI). DMSO, dimethyl sulfoxide. (C) Vector-MCF10A and CD8-IGF-IR-MCF10A cells were incubated with (+) or without (−) 1 μM BMS-536924 for 24 h in growth media. The levels of E-cadherin mRNA were examined by Q-PCR. The results are presented as relative transcript levels compared to vector-MCF10A by using the ΔΔCT method, with β-actin mRNA levels used as the normalization control. The error bars represent the standard errors of the means. (D) Vector-MCF10A and CD8-IGF-IR-MCF10A cells were incubated with (+) or without (−) BMS-536924 for 24 h and lysed, and the levels of epithelial (E-cadherin) or mesenchymal markers (vimentin and α-SMA) were measured. β-Actin was used as a loading control.
