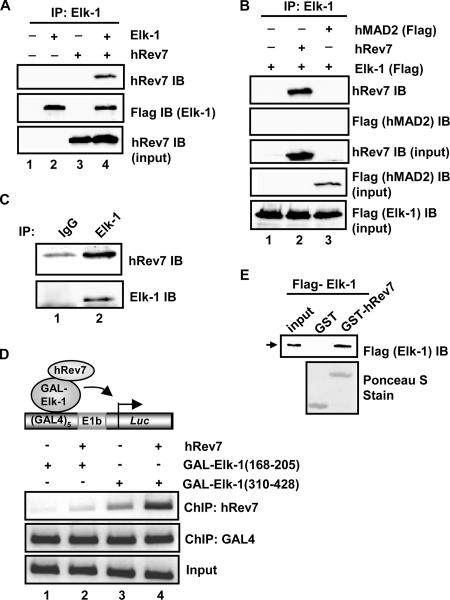
FIG. 1.
Elk-1 interacts with hRev7 in vivo and in vitro. (A) Coimmunoprecipitation of hRev7 with Elk-1 from 293T cells. Cells were transfected (+) with constructs encoding Flag-Elk-1 (2 μg) and/or hRev7 (3 μg) where indicated. Elk-1 proteins were immunoprecipitated (IP) by Elk-1 antibody, and precipitated proteins were detected by immunoblotting (IB) using hRev7 or Flag (for Elk-1) antibodies. (B) Coimmunoprecipitation was performed as described above for panel A, but Flag-tagged hMAD2 was also transfected with Elk-1 where indicated. (C) Coimmunoprecipitation of endogenous Elk-1 and hRev7 proteins with Elk-1 antibody from HeLa cells. Immunoglobulin G (IgG) antibody was used as a control. Proteins were detected by the indicated antibodies (IB). (D) ChIP analysis of hRev7 on an Elk-1-driven promoter. A GAL4-driven E1b promoter-reporter construct and the indicated GAL4-Elk-1 constructs were transfected into 293T cells in the presence (+) and absence (−) of full-length hRev7. The indicated antibodies were used for precipitation of different proteins (ChIP), and coprecipitating DNA was detected by PCR. (E) GST pulldown analysis of Elk-1 interaction with hRev7. GST-hRev7 or GST alone was used in a GST pulldown assay with full-length Flag-tagged Elk-1 that had been expressed and purified from bacteria. Bound Elk-1 was detected by IB using an anti-Flag antibody.