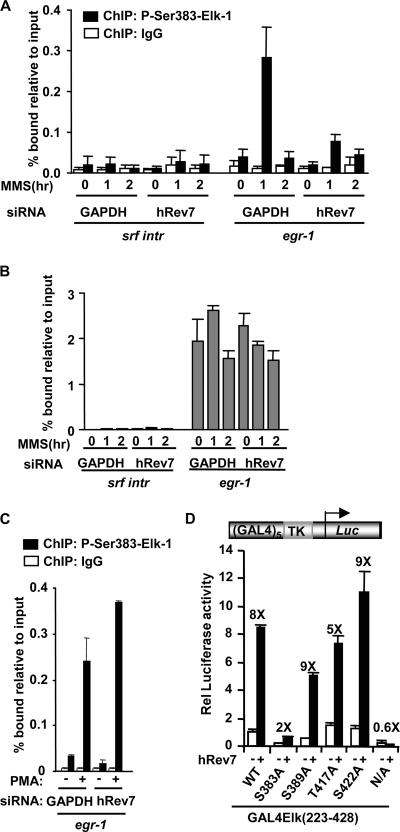
FIG. 4.
hRev7 enhances Elk-1 phosphorylation in vivo. (A to C) ChIP assays of phosphorylated and total Elk-1 upon hRev7 depletion. (A) ChIP assays of MMS-induced phosphorylated Elk-1. ChIP was performed with immunoglobulin G (IgG) (white bars) or anti-phospho-Ser383 Elk-1 (black bars) antibodies on extracts from HeLa cells transfected with siRNA duplexes against GAPDH or hRev7 and stimulated with MMS for the indicated times. Promoter DNA corresponding to srf intron 3 (SRF intr) or the egr-1 promoter was detected by real-time PCR. Experiments were performed in duplicate, and data are the averages of two experiments. (B) ChIP assays of total Elk-1 following MMS stimulation as described above for panel A, except that ChIP was performed with an anti-Elk-1 antibody. (C) ChIP assays of phosphorylated Elk-1 following PMA stimulation as described above for panel A, except that cells were stimulated with PMA (+) rather than MMS for 35 min where indicated. (D) Luciferase reporter analysis of hRev7 activation of Elk-1 mutants in 293T cells. GAL4-driven TK promoter-reporter plasmids (0.25 μg) were transfected into cells with the indicated wild-type (WT) and mutant GAL4-Elk-1(223-428) constructs (0.2 μg). Plasmids encoding hRev7 (1.5 μg) were added where indicated (+). Experiments were performed in duplicate and averaged from three independent experiments. The change in stimulation by hRev7 is given above each set of bars. Rel, relative; N/A, nine MAP kinase sites mutated to alanine.