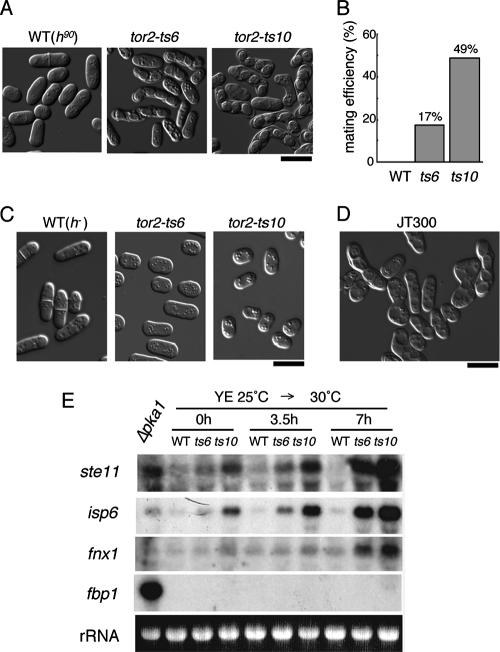
FIG. 2.
Sexual development of tor2-ts cells grown at the restrictive temperature. (A) The three homothallic haploid strains analyzed in the experiment shown in Fig. 1B were examined microscopically after 24 h of incubation at the restrictive temperature. Bar, 10 μm. (B) Calculated mating efficiency of the three strains shown in panel A. (C) Cells of heterothallic haploid strains incubated at the restrictive temperature for 24 h. wt, JY333; tor2-ts6, JV304; and tor2-ts10, JV306. Bar, 10 μm. (D) Cells of a homothallic strain JT300, in which tor2 is driven by the nmt81 promoter, were grown vegetatively on MM plates (− thiamine). They have undergone mating and sporulation even before shutoff of the promoter. Bar, 10 μm. (E) Expression of starvation-responsive genes in tor2-ts cells. Expression of three nitrogen starvation-responsive genes (ste11, isp6, and fnx1), and one glucose starvation-responsive gene (fbp1) was measured in wt (JY333), tor2-ts6 (JV304), and tor2-ts10 (JV306) cells at time zero and 3.5 and 7 h after the shift to the restrictive temperature. Their expression in pka1-defective cells (JX384) was also examined. rRNA stained with ethidium bromide is shown as a loading control.