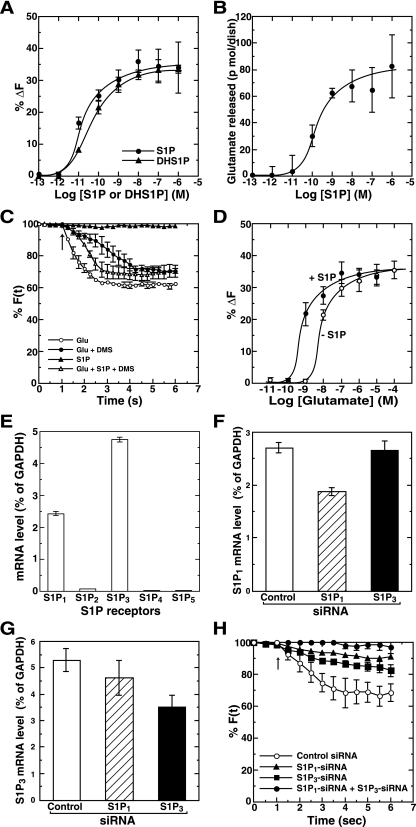
FIG. 6.
Functional roles of exogenous S1P as both an inducer and an enhancer of secretion. (A) Primary rat hippocampal neurons were prelabeled with FM4-64. FM dye-labeled cells were stimulated with various concentrations of either S1P or DHS1P for 6 s, and the changes in fluorescence intensity were monitored. At all points vehicle (methanol) concentrations were kept constant. (B) Neurons washed three times with PBS were stimulated with various concentrations of S1P for 6 s. Secreted glutamate was measured by an enzymatic fluorometric assay. (C) Neurons were treated without (vehicle) or with 10 μM DMS for 30 min and labeled with FM dye. Neurons were then stimulated with various combinations of 1 pM S1P and 100 μM glutamate for the indicated time, and the changes in fluorescence intensity were monitored. The arrow indicates the addition of agonists. (D) FM dye-prelabeled neurons were treated with various concentrations of glutamate without or with 1 pM S1P for 6 s, and the changes in fluorescence intensity were monitored. (E) Individual S1P receptor mRNAs were quantitated from primary rat hippocampal neurons by real-time quantitative reverse transcription PCR. Values of mRNA amounts were normalized to GAPDH expression. (F and G) Hippocampal neurons were transfected with control or S1P1 or S1P3 siRNA. Two days after transfection S1P1 mRNA (F) or S1P3 mRNA (G) levels were quantitated by real-time quantitative reverse transcription PCR. (H) Hippocampal neurons transfected with various combinations of control or S1P1 and S1P3 siRNAs were prelabeled with FM4-64. Neurons were stimulated with 10 nM S1P, and the changes in fluorescence intensity were monitored. The arrow indicates the addition of S1P. Data are the means ± standard errors of the means of five independent experiments carried out three (A to D and H) or six (E) times. For F(t), fluorescence at the selected region at time t, see text.