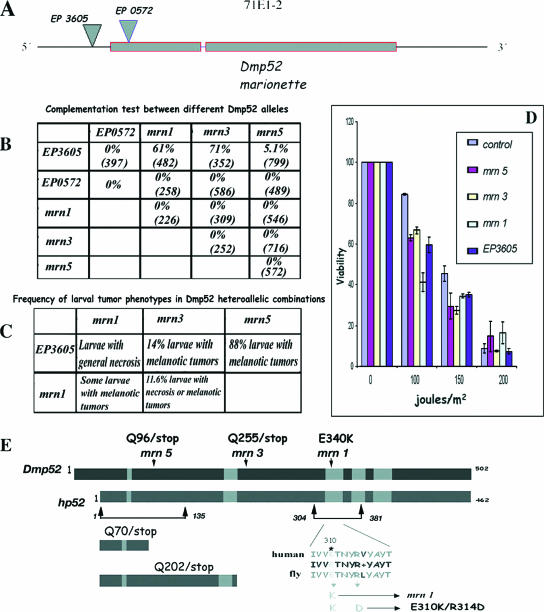
FIG. 1.
Genetic and molecular description of Dmp52 alleles, complementation tests, and UVB irradiation sensitivity assay. (A) Genomic organization of the Dmp52 (mrn) gene and EP insertions. Dmp52 contains two coding exons and a short intron. Dmp52 maps in the cytological position 71E1-2. The positions of the two EP insertions are shown by inverted triangles. EP3605 is inserted at the 5′ end of the gene 20 nucleotides from the start codon. EP0572 is inserted in the first intron of the Dmp52 gene, 5 nucleotides after the start codon, disrupting the DMP52 protein. (B) Complementation test between different mrn point mutations and the EP insertions. The percentage represents the adult flies observed in the expected class. The number in parentheses is the number of expected individuals for each class. Only EP3605 is able to complement, at least partially, the three different mrn point mutation alleles. The other allele combinations are lethal, including EP0572. (C) Frequency of larval tumor phenotypes in the Dmp52 heteroallelic combinations. The percentage represents the larvae observed to have any tumor compared to the healthy class. In the case of the EP3605 allelic combinations, the unaffected populations are presumably those that continue development until adulthood. The larvae of the allelic combinations including at least one copy of Dmp52 (E340K) mrn1 were not quantified. (D) Viability test of the Dmp52 mutants and the parental strain after different UVB irradiation doses. Third-instar larvae heterozygous for Dmp52 mutants were irradiated and then allowed to develop until adulthood. The survival rate is indicated for each strain. The graph represents the results of at least six independent dosage experiments for each genotype. The statistical analysis by analysis of variance indicated a P value of <0.0001 for each mutant compared with the parental strain at 100 and 150 J/m2. The error bars indicate standard errors. (E) Molecular characterization of the Dmp52 point mutants and diagram showing the mutations characterized in the Dmp52 gene introduced into hp52. The gray boxes indicate the regions with highest similarity between the DMP52 and HP52 proteins. The amino acid changes found in the mrn1 (E340K), mrn3 (Q225/stop), and mrn5 (Q96/stop) alleles are indicated by arrows. Truncated peptides, as well as the single and double amino acid changes analyzed in the HP52 protein, are also indicated.