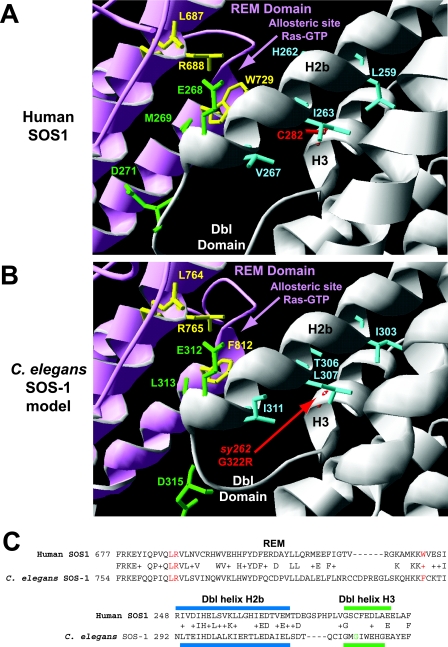
FIG. 3.
Conservation of the Dbl and REM domains between human and C. elegans SOS proteins. (A) Crystal structure of the Dbl-PH-REM-CDC25 domains from hSOS1 at 3.62 Å (84). The yellow residues (L687, R688, and W729) indicate amino acids in the REM domain that interact with Ras-GTP and are important for Ras-GTP-dependent allosteric stimulation of CDC25 activity. The green residues in the Dbl helix H2b (E268 and M269) and loop (D271) contribute to autoinhibition of the REM domain. Substitution mutations converting all three green amino acids to alanines result in a protein that is hypersensitive to allosteric activation (84). The blue residues (L259, H262, I263, and V267) in helix H2b point toward the surface of helix H3. C282 in helix H3 is in the position analogous to that of the sy262 G322R mutation in the C. elegans Dbl domain. SWISS-MODEL modeling suggested that a C282R change might not be compatible with the normal geometry of the blue residues in helix H2b. (B) SWISS-MODEL of the C. elegans Dbl-PH-REM-CDC25 domains from SOS-1. Note the conservation of the yellow residues (L764, R765, and F812) in the REM domain for allosteric stimulation of CDC25 activity by Ras-GTP, conservation of the green residues (E312, L313, and D315) in the Dbl domain for potential autoinhibition of the REM domain, and conservation of the blue bulky/hydrophobic residues (I303, T306, L307, and I311) that face the surface of Dbl helix H3. SWISS-MODEL modeling suggests that the G322R change in helix H3 may not be compatible with the predicted geometry of the blue residues in helix H2b. (C) BLAST alignments of relevant portions of the REM and Dbl domains between human and C. elegans SOS proteins. The red amino acids in the REM domain are important for binding Ras-GTP. The blue bar indicates the position of Dbl helix H2b (predicted in C. elegans), and the green bar indicates the position of Dbl helix H3 (predicted in C. elegans). The green amino acid is the locations of the sy262 mutation. Plusses indicate conservative amino acid changes between the human and C. elegans proteins.