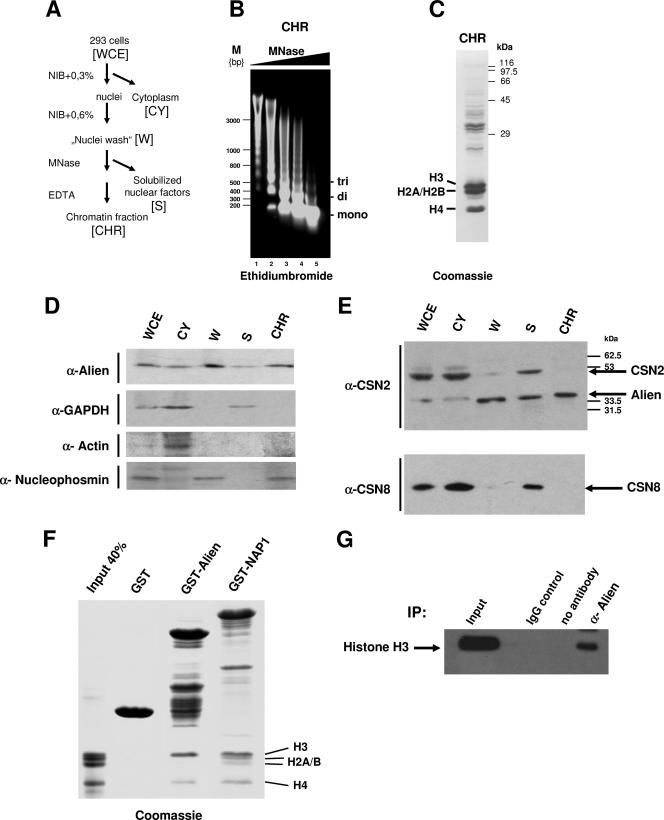
FIG. 3.
Alien is associated with chromatin in vivo. (A) Schematic view of the chromatin fractionation including MNase digestion of human embryonal kidney cell line HEK293. (B) Ethidium bromide staining of the isolated genomic DNA from the chromatin fractions after incubation with increasing amount of MNase. Depicted are the migrations of DNA fragments corresponding to DNA wrapped around mono-, di-, and trinucleosomes. (C) Coomassie staining of the chromatin fraction confirms the presence of the core histones as major components. (D) Western analysis of the fractions performed with antibodies specific for Alien, GAPDH, actin, and nucleophosmin revealed the specific presence of each protein. (E) Identification of the signalosome subunits CSN2 and CSN8 in the fractions. The anti-CSN2 antibody recognized both Alien and CSN2. (F) GST or the indicated GST fusions were incubated with the histones H3, H2A, H2B, and H4. The input lane corresponds to 40% of the histones used. After several washing steps, bound proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE and visualized by Coomassie staining. NAP1 interacts with all four core histones whereas Alien interacts specifically with histones H3 and H4. (G) Immunoprecipitation of Alien with histone H3 from HEK293 cells. IgG and the beads alone (no antibody) were used as internal controls for immunoprecipitation (IP); Western analyses were performed with histone H3 antibody. WCE, whole-cell extracts; CY, cytoplasmic fraction; W, supernatant of nuclei washing steps; S, solubilized nuclear factors after MNase digestion; CHR, chromatin fraction; α, anti; M, molecular size marker.