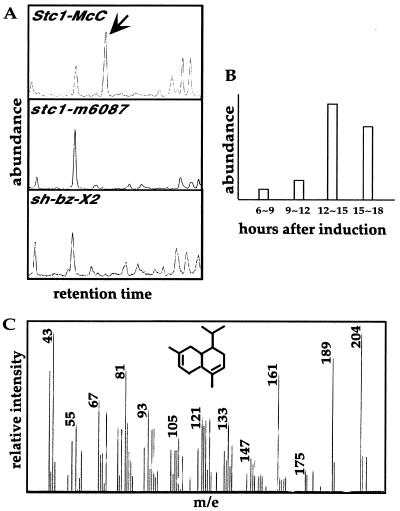
Figure 5.
GC profiles of volicitin-induced volatiles in various genotypes. (A) At 10-days-old, seedlings were cut above the root, immediately immersed in a volicitin solution, and kept in complete darkness for 12 h. Volatiles were collected from treated seedlings in a special chamber provided with artificial light and purified air. GC profiles are for volatiles from wild type (Stc1-McC), the Ac insertion mutation stc1-m6087, and the deletion mutation sh-bz-X2. The unique peak in wild type is indicated by an arrow. This experiment was repeated three times with the same result. (B) Time course production of the Stc1-McC-specific compound from wild-type seedlings. The induction treatment was the same as above. (C) MS identification of the Stc1-McC-specific compound. The unique peak in the Stc1-McC GC was analyzed by MS. The MS spectrum of the Stc1-McC-specific compound matched that of the sesquiterpenoid naphthalene, 1,2,4a,5,8,8a–hexahydro-4,7-dimethyl-1-(1-methylethyl)-,(1α,4aβ,8aα) from the chemical database (Inset).