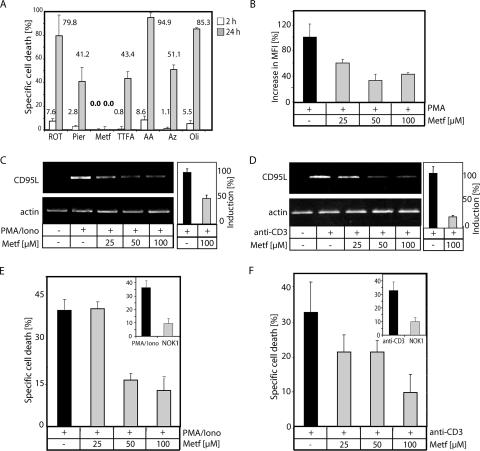
FIG. 8.
Metformin, a nontoxic complex I inhibitor, blocks activation-induced oxidative signal, CD95L expression, and AICD. (A) Metformin induces no toxicity. J16-145 cells were treated for 2 h (white bars) and 24 h (gray bars) with the indicated inhibitors (ROT, rotenone [10 μg/ml]; Pier, piericidin A [7.5 μM]; Metf, metformin [100 μM]; TTFA, 1,1,1-thenoyl trifluoroacetone [25 μM]; AA, antimycin A [4 μg/ml]; Az, sodium azide [100 μg/ml]; OLI, oligomycin [10 μg/ml]). Cell death was determined by a drop in the FSC/SSC profile in comparison to living cells and recalculated to specific cell death. (B) J16-145 cells were pretreated with the indicated amounts of metformin, stained with DCFDA, and stimulated by PMA for 30 min. Oxidative signal was quantified as the increase in MFI. (C and D) J16-145 cells were pretreated with the indicated amounts of metformin and stimulated with PMA/ionomycin (Iono) (C) or plate-bound anti-CD3 antibodies (D) for 1 h. Next, RNA was isolated, reverse transcribed, and amplified with CD95L- and actin-specific primers (left). In addition, a quantitative PCR was performed (right). CD3-induced CD95L expression was set to 100%. All other values were calculated according to the CD3-induced CD95L expression. (E and F) J16-145 cells pretreated with the indicated amounts of metformin and AICD were induced by PMA/ionomycin (Iono) treatment (E) or stimulation with plate-bound anti-CD3 antibodies (F). After 24 h, cell death was assessed by the drop in the FSC/SSC index. Inserts show J16-145 cells cotreated with or without CD95L neutralizing antibody (NOK1) and stimulated by plate-bound anti-CD3 antibodies. Results were recalculated to specific cell death.