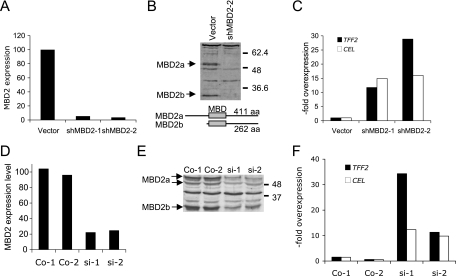
FIG. 4.
Depletion of MBD2 induces ExPa gene expression in a human colon cell line. (A) Real-time RT-PCR analysis for MBD2 expression levels in a mock-transfected HCT116 cell clone (vector) and two stable derivate cell lines expressing shRNA directed against MBD2 (shMBD2-1 and shMBD2-2). (B) Western blot analysis for MBD2 in cell extracts from mock-transfected cells (vector) and a cell clone expressing shRNA for MBD2 (shMBD2-2). The structure and length of the MBD2a and MBD2b isoforms is indicated below. (C) Real-time RT-PCR analysis of ExPa gene expression in control cells and cells stably expressing shRNA against MBD2. Values indicate the overexpression normalized to the vector control. (D) Moderate (four- to fivefold) reduction of MBD2 mRNA levels by siRNA knockdown in two transfected cell lines si-1 and si-2) and two mock-transfected control cell lines analyzed by real-time RT-PCR. (E) Western blot analysis of MBD2 isoform confirms partial depletion in the two siRNA-transfected cell lines. Wild-type levels of MBD2 are seen in control cell lines (Co-1 and Co-2). (F) Real-time RT-PCR analysis of TFF2 and CEL gene expression levels in control and MBD2-depleted HCT116 cells.