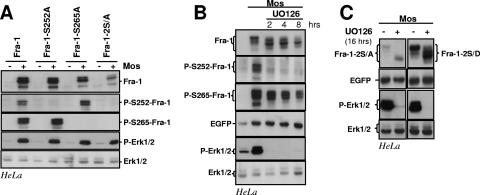
FIG. 4.
Erk1/2 pathway-induced phosphorylations of S252 and S265 and Fra-1 stabilization. (A) Erk1/2 pathway-induced phosphorylations of Fra-1 S252 and S265. HeLa cells were transfected to express the indicated proteins (Fig. 2A) in the presence or in the absence of Mos. Total cell extracts were probed with the various rabbit antisera designated for the detection of total Fra-1 (Fra-1), S252-phosphoylated Fra-1 (P-S252-Fra-1), and S265-phosphorylated Fra-1 (P-S265-Fra-1) as well as total Erk1/2 and phosphorylated Erk1/2 (P-Erk1/2). The differences in Fra-1-2S/A abundances in the presence and in the absence of Mos result largely from differences in the transcriptional activity of the expression vector as shown in Fig. 3. (B) UO126 chase of HeLa cells coexpressing Fra-1 and Mos. The UO126 chase was started 16 h after cotransfection of asynchronous HeLa cells transfected with Fra-1 and Mos expression vectors. Immunoblotting experiments were conducted with extracts from cells taken at various time points. (C) UO126 chase in HeLa cells coexpressing Mos with either Fra-1-2S/A or Fra-1-2S/D. The experiment was carried out as in B. + corresponds to 8 h in the presence of UO126. The data presented are representative of three independent experiments.