FIG. 1.
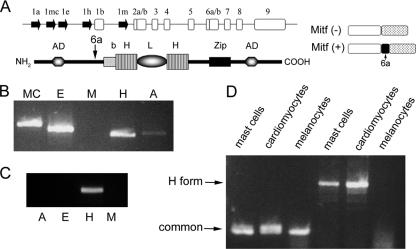
Expression of various Mitf isoforms. (A) Genomic organization of the mi locus and the structure of Mitf protein. The genomic organization of the Mitf gene is depicted (top). Filled arrows represent alternative promoters. Empty boxes represent common exons. The structure of Mitf protein is depicted below: b, basic domain; HLH, helix-loop-helix; Zip, leucine zipper; AD, activation domain. The location of the alternatively spliced exon 6a is indicated by an arrow. The structures of Mitf-(−) and Mitf-(+) are also depicted (right). (B) Expression of Mitf isoforms in bone marrow-derived mast cells. Variable 5′ primers from exons 1mc, 1e, 1m, 1h, and 1a and from the common exon 2 were amplified by PCR. (C) Expression of Mitf isoforms in normal heart of mice. Variable 5′ primers from exons 1e, 1m, 1h, and 1a and from the common exon 2 were amplified by PCR. (D) Expression of Mitf and Mitf-H in mast cells, melanocytes, and primary cardiomyocytes. Mitf was amplifed by PCR using primers from the common exon 5 to exon 7 (common; lanes 1 to 3 from the left), and Mitf-H was amplified by PCR using different primers for exon 1h to exon 1b (H form; lanes 4 to 6).