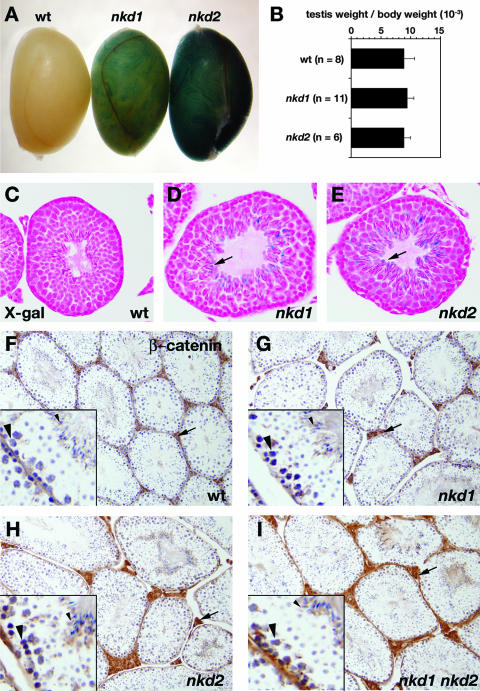
FIG. 5.
nkd mutant testes resemble wild-type testes. (A) X-Gal-stained wild-type (wt, left), nkd1lacZ/lacZ (middle), and nkd2lacZ/lacZ (right) testis tissues from 3-month-old males. (B) Ratios of combined testis weight to body weight for the indicated numbers of 3-month-old wild-type (top bar) and homozygous nkd1 (middle bar) or nkd2 (bottom bar) mutant male mice. (C to E) High-power magnifications of X-Gal-stained testis tubules from wild-type (C), nkd1lacZ/lacZ (D), and nkd2lacZ/lacZ (E) mice. Note the X-Gal-positive elongating sperm near the tubular lumen (arrows) in panels D and E. (F to I) β-Catenin immunohistochemistry of wild-type (F), nkd1lacZ/lacZ (G), nkd2lacZ/lacZ (H), and nkd1lacZ/lacZ nkd2lacZ/lacZ (I) testes revealed by DAB staining (brown) shows similar distribution and intensity of intertubular (Leydig cell, arrow) staining, as well as basal spermatocyte nuclei (large arrowhead in lower left of each inset) and elongating spermatids (small arrowhead in upper right of each inset). Note the similar staining of all four genotypes.