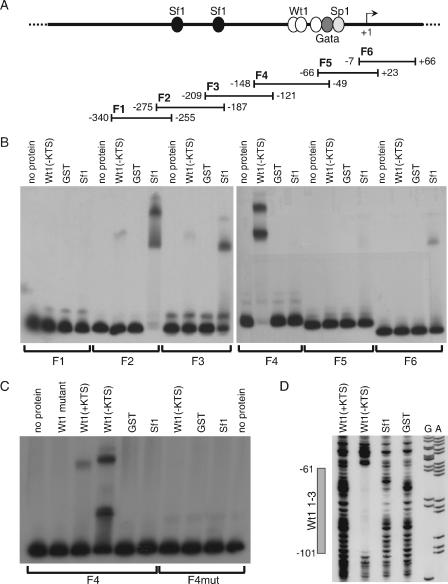
FIG. 5.
Wt1(−KTS) and Sf1 bind to the murine Amhr2 promoter in vitro. (A) Schematic representation of the Amhr2 promoter, containing potential transcription factor binding sites, and the fragments used for EMSA. (B) For EMSA analysis, labeled fragments F1 to F6 were incubated without protein and with recombinant GST, GST-Wt1(−KTS), and GST-Sf1. (C) Wild-type and mutated F4 were additionally analyzed by adding GST-Wt1(+KTS) and a mutant form of GST-Wt1(−KTS). F4 was mutated by replacing three of the five conserved cytosines with adenines in all three Wt1 binding sites. (D) Binding of Wt1 to the consensus binding sites was also shown by DNase footprinting analysis using the same recombinant proteins and a 5′-labeled PCR fragment. Sequencing reactions for A and G bases of the same fragment are shown. The gray box indicates the region protected by Wt1(−KTS) spanning all three consensus binding sites. Numbers in panels A and D refer to the murine Amhr2 promoter sequence (53).