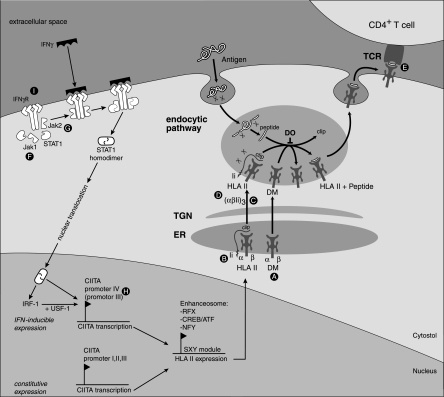
FIG. 1.
Herpesvirus downregulation of HLA class II expression. Posttranscriptional interference: HCMV US2-mediated dislocation and subsequent degradation of HLA-DRα and DMα (A) results in decreased formation of HLA class II-Ii complexes in the ER and impaired loading of HLA class II with peptide downstream from the Golgi apparatus. Displacement of Ii by HSV gB (B) results in impaired peptide loading. HCMV US3 (C) causes retention of HLA class II-Ii complexes in the Golgi apparatus while HCMV pp65 (D) targets HLA class II complexes to abnormal perinuclear lysosomes. HLA class II-TCR interactions are inhibited by EBV gp42 (E). Other gene products of note are HSV γ34.5 and UL41, which act by an unknown mechanism (consequently, not shown). Pretranscriptional interference (affecting IFN-γ-induced expression only): interference with the function of IFN-γ-associated signaling molecules occurs during infection with HCMV (Jak1 [F]), HSV-1 (STAT1, STAT2, and Jak1 [F]), and also VZV (STAT1α and Jak2 [G]). Further inhibition occurs downstream at the level of CIITA promoter IV during HCMV infection (H). The EBV BZLF1 gene product decreases the levels of IFN-γ receptor α, thereby shutting down the entire IFN-γ-induced CIITA signaling cascade (I). HLA II, HLA class II; TGN, trans-Golgi network; RFX, regulatory factor x; ATF, activating transcription factor; IRF-1, IFN regulatory factor 1; USF-1, upstream stimulatory factor 1.