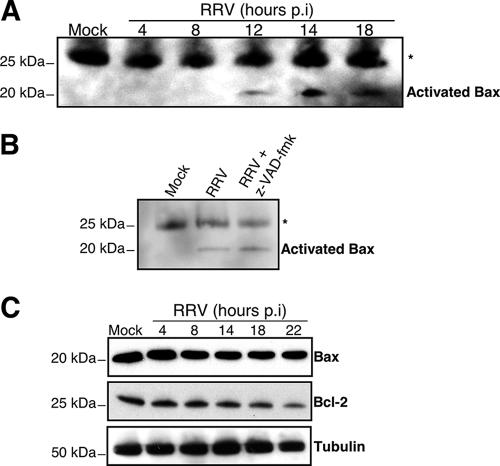
FIG. 5.
RRV induces Bax protein activation in MA104 cells. (A) RRV induced a conformational change in Bax in MA104 cells. At the indicated time p.i., MA104 cells were lysed in immunoprecipitation buffer containing the zwitterionic detergent CHAPS (which maintains Bax in its activated conformation). The anti-Bax antibody 6A7 was used to immunoprecipitate conformationally active Bax protein. The immunoprecipitates were analyzed by immunoblotting with an anti-Bax antibody. Asterisk indicates immunoglobulin light chains. Mock-infected MA104 cells were used as negative controls. Positions of molecular weight markers are indicated on the left. (B) z-VAD-fmk did not inhibit Bax conformational change in RRV-infected MA104 cells. RRV-infected MA104 cells either were not pretreated or were pretreated with 100 μM z-VAD-fmk for 2 h before infection, and treatment was continued during infection. Whole-cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with an activated Bax antibody (clone 6A7) and then analyzed by immunoblotting with an anti-Bax antibody. Mock-infected MA104 cells were used as negative controls. Asterisk indicates immunoglobulin light chains. Positions of molecular weight markers are indicated on the left. (C) RRV infection promoted Bcl-2 degradation in MA104 cells. At the indicated times p.i., whole-cell lysates were prepared. Bax and Bcl-2 proteins were detected by Western blotting with anti-Bax and anti-Bcl-2 specific antibodies. Mock-infected MA104 cells were used as negative controls. Tubulin was used as a control for protein loading. Positions of molecular weight markers are indicated on the left.