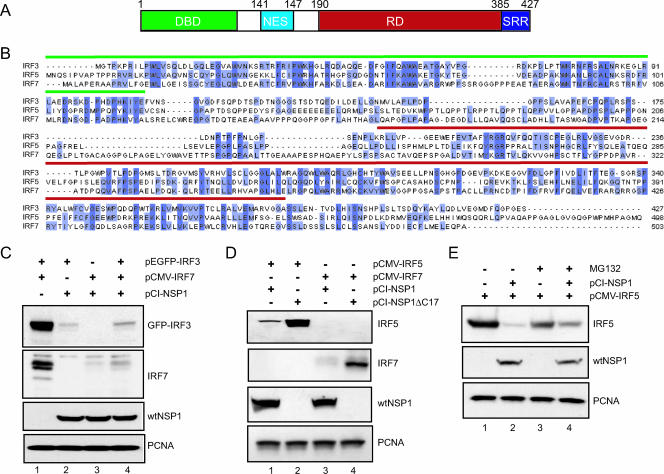
FIG. 7.
Members of the IRF family as targets of NSP1. (A) Schematic representation of the structural domains of the IRF3 protein: DBD DNA-binding domain; NES, nuclear export signal; RD, regulatory domain; and SRR, serine-rich region. (B) Sequence alignment of human IRF3 (accession number Q14653), IRF5 (Q92985), and IRF7 (NM_032643). The DNA-binding domains and regulatory domains are overlined in green and red, respectively. Conserved residues are highlighted in dark blue. Residues present in two of the three sequences are shown in light blue. (C) EGFP-IRF3 and IRF7 were transiently expressed individually or in combination with NSP1 in 293T cells by transfection with the indicated plasmids. The levels of EGFP-IRF3, IRF7, wt NSP1, and PCNA were determined by Western blot assay. After 48 h, the cells were examined for levels of IRF3, IRF7, wt NSP1, and PCNA by Western blot assay. (D) IRF5 and IRF7 were individually expressed with wt NSP1 or NSP1ΔC17 in 293T cells by transfection with the indicated plasmids. After 48 h, the cells were examined for levels of IRF5, IRF7, wt NSP1, and PCNA by Western blot assay. (E) 293T cells were transfected with pCMV-IRF5 alone or in combination with pCI-NSP1. At 48 h posttransfection, the culture medium was adjusted to 10 μM MG132. Cell lysates were prepared 12 h later and then analyzed by Western blot assay for IRF5, wt NSP1, and PCNA.