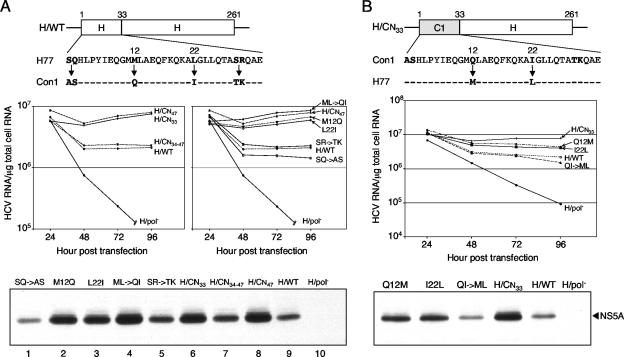
FIG. 4.
Enhancing residues map to the N-terminal 33 amino acids of Con1 NS4B. (A) Replicative abilities of H77 replicons expressing hybrid or mutant NS4B proteins. (Top) Schematic representation of H77 NS4B, with the first 33 amino acids of H77 and Con1 NS4B aligned below. Divergent residues are boldfaced, and arrows indicate the amino acid substitutions tested. (Center) Huh-7.5 cells were electroporated with the parental H/WT replicon, H77 chimeric RNAs (H/CN47, H/CN33, and H/CN34-47) (Fig. 1), and H77 replicons containing the S1A and Q2S (SQ→AS), M12Q, L22I, M12Q and L22I (ML→QI), or S29T and R30K (SR→TK) mutations. At the indicated times postelectroporation, HCV RNA levels were measured as described above. At the 96-h time point, 9 × 104 RNA copies per μg of total cellular RNA were detected in H/pol−-transfected cells. (Bottom) Western blot analysis of NS5A expression levels at 96 h posttransfection. Similar results were obtained in four independent experiments. (B) HCV RNA and NS5A levels of the H77 chimeric replicon H/CN33 (Fig. 1), containing the Q12M or the I22L mutation or both (QI→ML). (Top) Diagram of the hybrid NS4B protein containing the first 33 amino acids of Con1 NS4B fused to the remaining H77 NS4B sequence. Shown below is the alignment of the N-terminal 33 residues of Con1 and H77 NS4B, with the divergent residues boldfaced; the amino acid replacements analyzed are indicated by arrows. (Center) HCV RNA levels quantified at 24 to 96 h after transfection of Huh-7.5 cells. (Bottom) NS5A expression at 96 h after RNA transfection. These results are representative of two repetitions of the experiment.