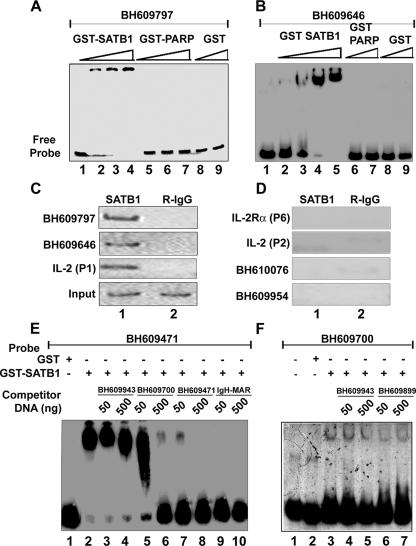
FIG. 1.
SATB1 specifically binds to HIV-1 integration sequences in vitro and in vivo. In vitro binding of SATB1 to HIV-1 integration clones BH609797 (A) and BH609646 (B) was demonstrated by EMSA as described in Materials and Methods. Briefly, 10 to 100 ng of recombinant purified GST-SATB1, GST-PARP, or GST was incubated as indicated with radiolabeled, PCR-amplified DNA probes in the presence of 1 μg of competitor DNA. Protein-DNA complexes were resolved on native polyacrylamide gels. In vivo binding of SATB1 was demonstrated by PCR amplification of DNA isolated by ChIP (C and D) with anti-SATB1 (lane 1) or rabbit IgG (R-IgG; lane 2). Distal promoter region P1 of IL-2 was used as a positive control for SATB1 binding, whereas proximal promoter region P2 of IL-2 and region P6 of IL-2Rα were used as negative controls. ChIP analysis of two representative in vivo integration clones, BH609797 and BH609646 (C), and two representative in vitro integration clones, BH610076 and BH609954 (D), is depicted. The specificity of binding of SATB1 to HIV-1 in vivo integration clones BH609471 (E) and BH609700 (F) was demonstrated by competition EMSA. Briefly, 2 μg of recombinant purified GST-SATB1 (lanes 2 to 10 in panel E and lanes 3 to 7 in panel F) or GST alone (lane 1 in panel E and lane 2 in panel F) was incubated with radiolabeled, PCR-amplified DNA probes in the presence of 1 μg of poly(dI-dC) competitor DNA. Protein-DNA complexes were resolved on 6% native polyacrylamide gels. Binding reactions were competed for by adding a 10-fold (50 ng) or 100-fold (500 ng) excess of unlabeled, PCR-amplified homologous or heterologous DNA to the binding reaction mixture as indicated.