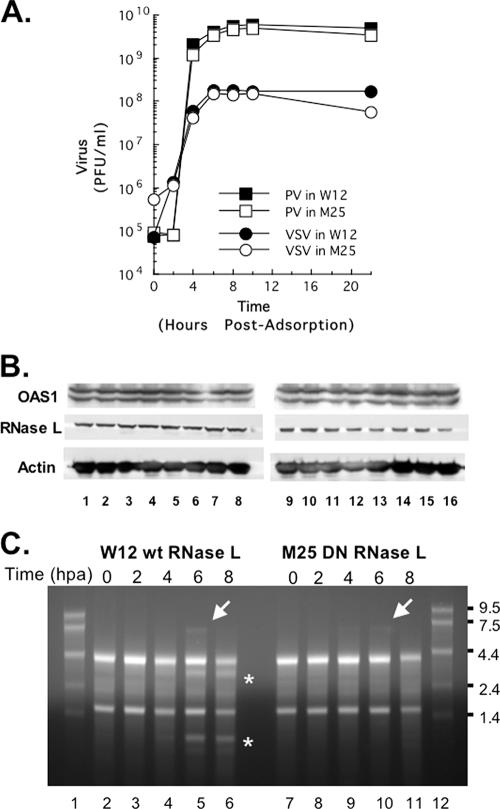
FIG. 8.
One-step growth reveals activation of RNase L late during the course of PV replication. HeLa M cells overexpressing wild-type RNase L (W12) or a DN mutant RNase L (M25) were infected with wild-type PV or VSV at an MOI of 5. (A) Virus titers were determined at 0, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, and 22 h postadsorption by plaque assay after freeze-thawing to release intracellular virus. (B) OAS1 and RNase L expression was examined by Western blotting with chemiluminescence, as described in Materials and Methods. Proteins from uninfected cells (lanes 1 and 9) and cells at 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, and 6 h postadsorption (lanes 2 to 8, W12 HeLa cells; lanes 10 to 16, M25 HeLa cells) were examined. Western blotting of actin in each sample was determined as a loading control. (C) Total cellular RNA was isolated at 0, 2, 4, 6, and 8 h postadsorption (hpa) from PV-infected W12 cells (lanes 2 to 6) or PV-infected M25 cells (lanes 7 to 11). RNA size markers were fractionated in lanes 1 and 12. RNAs were separated by electrophoresis in 1% agarose, stained with ethidium bromide, and visualized with UV light. Asterisks highlight the mobility of rRNA fragments characteristic of RNase L cleavage. Arrows indicate the mobility of PV RNA.