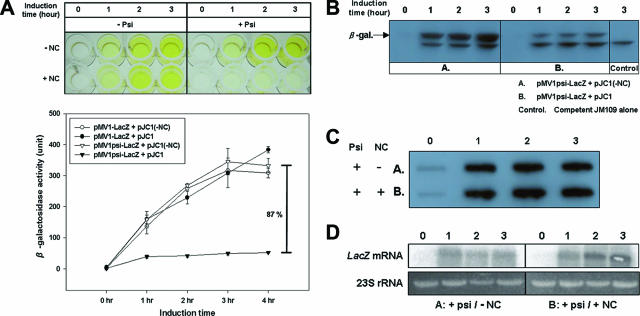
FIG. 1.
Translation inhibition caused by the HIV type 1 (HIV-1) NC-Ψ interaction. (A) Visualization and quantitative analysis of the ONPG assay for translation inhibition due to the interaction of HIV-1 NC and Ψ RNA. JM109 was doubly transformed with the indicated individual vectors shown in the insert, and their lacZ reporter gene activities were determined by ONPG assay. (B) Western blot analysis of the expression of β-galactosidase. A and B indicate JM109 cells cotransformed with pMV1psi-LacZ containing Ψ sequence and pJC1(-NC) or pJC1, respectively. Control indicates nontransformed JM109 cells. The band in the control originates from the endogenous inactive partial lacZα peptide of JM109 (lacZΔM15) cells; it served as an internal control for the amounts of cell lysates used in the analysis. The cotransformants and JM109 were harvested at the indicated times after IPTG induction. Cell lysates were loaded onto a 10% sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel and subjected to Western blot analysis. (C and D) Slot blot (C) and Northern blot (D) analyses. Total RNA was prepared from cotransformants A and B as described above. Ten micrograms of DNase I-treated total cellular RNA was loaded onto each lane and subjected to slot blot and Northern analysis.