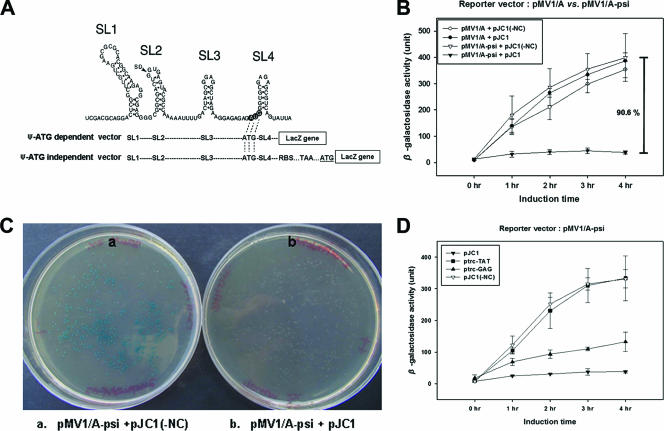
FIG. 2.
Translation inhibition assay with the Ψ-ATG-independent reporter vector. (A) Schematic representations of the sequence organizations upstream of the lacZ reporter gene in the Ψ-ATG-dependent and Ψ-ATG-independent vector systems. The possible secondary structure of the HIV-1NL4-3 Ψ sequence is shown at the top. The location of the HIV-1 splicing donor site is marked with an arrowhead, and the original translation start codon (AUG) of the HIV-1 Gag polyprotein is shown by open lettering in dark circles. Ψ-ATG-dependent vector refers to lacZ translation initiation starting from the AUG start codon located in the SL4 region of the Ψ sequence. The Ψ-ATG-independent vector initiates the translation of lacZ at its own AUG (underlined) downstream of Ψ RNA (see the text for more details). Dotted lines indicate the same sequence as that in the Ψ RNA sequence. (B) Effect of NC on Ψ-ATG-independent expression of lacZ. (C) Visualization of NC-Ψ-mediated lacZ translation inhibition on agar. The effect of the interaction between NC and the Ψ sequence on β-galactosidase expression in JM109 was monitored using agar plates containing 2% X-gal and 70 μM IPTG. At the left and right are JM109 transformants containing pMV1/A-psi without NC (a) and with NC (b), respectively. (D) Effect of Gag polyprotein and Tat protein on Ψ-ATG-independent expression of lacZ. The expression vectors used are indicated in the insert. All experiments were performed three times.